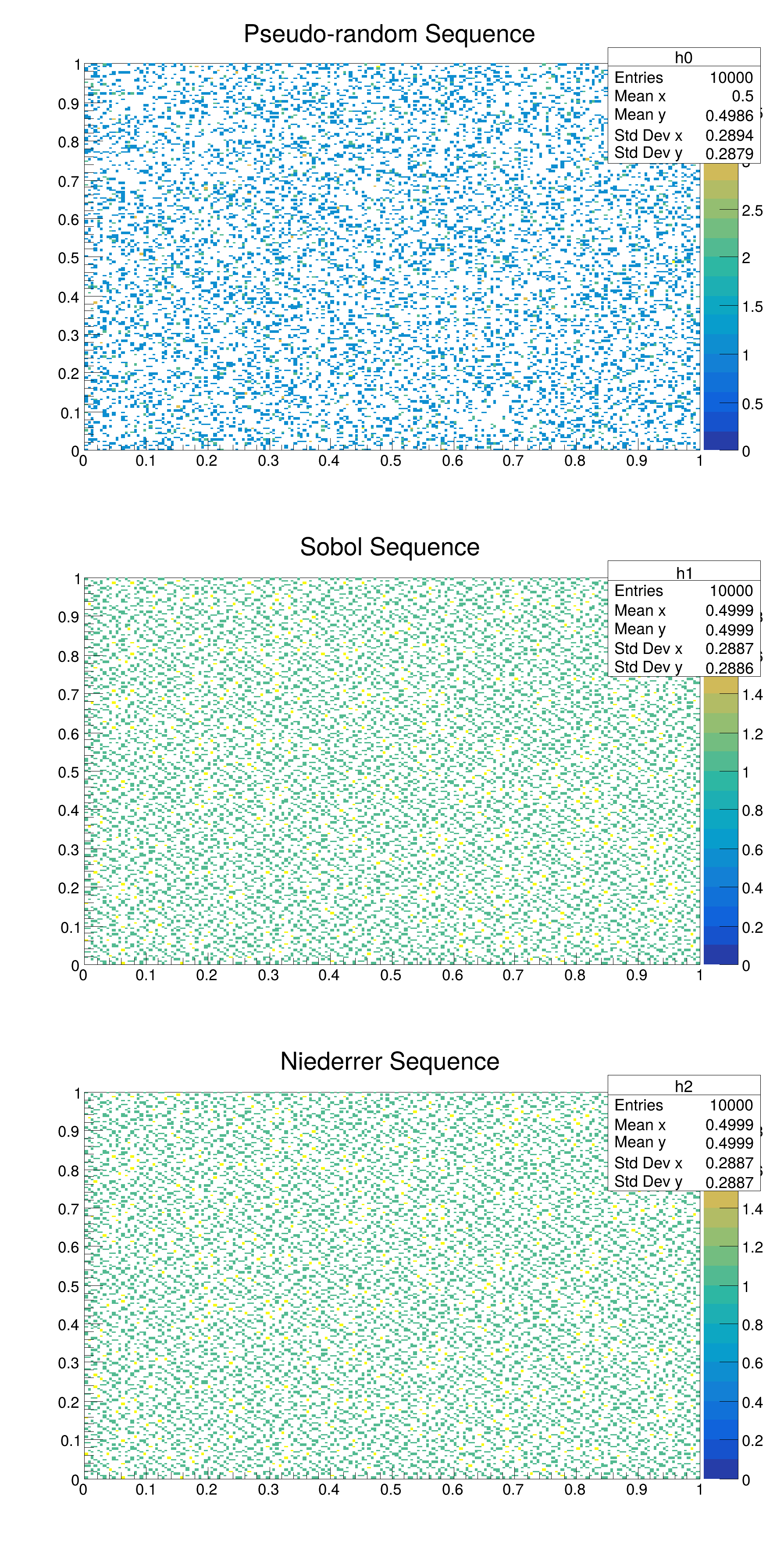
Example of generating quasi-random numbers
Time for gRandom Real time 0:00:00, CP time 0.000
Time for Sobol Real time 0:00:00, CP time 0.000
Time for Niederreiter Real time 0:00:00, CP time 0.000
number of empty bins for pseudo-random = 31139
number of empty bins for sobol = 30512
number of empty bins for niederreiter-base-2 = 30512
(int) 0
#include <iostream>
TH2D *
h0 =
new TH2D(
"h0",
"Pseudo-random Sequence",200,0,1,200,0,1);
TH2D *
h1 =
new TH2D(
"h1",
"Sobol Sequence",200,0,1,200,0,1);
TH2D * h2 =
new TH2D(
"h2",
"Niederrer Sequence",200,0,1,200,0,1);
for (
int i = 0; i <
n; ++i) {
}
std::cout << "Time for gRandom ";
for (
int i = 0; i <
n; ++i) {
}
std::cout << "Time for Sobol ";
for (
int i = 0; i <
n; ++i) {
}
std::cout << "Time for Niederreiter ";
}
}
std::cout <<
"number of empty bins for pseudo-random = " <<
nzerobins0 << std::endl;
std::cout <<
"number of empty bins for " <<
r1.Name() <<
"\t= " <<
nzerobins1 << std::endl;
std::cout <<
"number of empty bins for " <<
r2.Name() <<
"\t= " <<
nzerobins2 << std::endl;
}
ROOT::Detail::TRangeCast< T, true > TRangeDynCast
TRangeDynCast is an adapter class that allows the typed iteration through a TCollection.
virtual Int_t GetNbinsY() const
virtual Int_t GetNbinsX() const
virtual Int_t Fill(Double_t x)
Increment bin with abscissa X by 1.
void Draw(Option_t *option="") override
Draw this histogram with options.
virtual Double_t GetBinContent(Int_t bin) const
Return content of bin number bin.
2-D histogram with a double per channel (see TH1 documentation)
- Author
- Lorenzo Moneta
Definition in file quasirandom.C.