| library: libSpectrum #include "TSpectrumFit.h" |

| TSpectrumFit() | |
| TSpectrumFit(Int_t numberPeaks) | |
| TSpectrumFit(const TSpectrumFit&) | |
| virtual | ~TSpectrumFit() |
| void | TObject::AbstractMethod(const char* method) const |
| virtual void | TObject::AppendPad(Option_t* option = "") |
| virtual void | TObject::Browse(TBrowser* b) |
| static TClass* | Class() |
| virtual const char* | TObject::ClassName() const |
| virtual void | TNamed::Clear(Option_t* option = "") |
| virtual TObject* | TNamed::Clone(const char* newname = "") const |
| virtual Int_t | TNamed::Compare(const TObject* obj) const |
| virtual void | TNamed::Copy(TObject& named) const |
| virtual void | TObject::Delete(Option_t* option = "") |
| virtual Int_t | TObject::DistancetoPrimitive(Int_t px, Int_t py) |
| virtual void | TObject::Draw(Option_t* option = "") |
| virtual void | TObject::DrawClass() const |
| virtual TObject* | TObject::DrawClone(Option_t* option = "") const |
| virtual void | TObject::Dump() const |
| virtual void | TObject::Error(const char* method, const char* msgfmt) const |
| virtual void | TObject::Execute(const char* method, const char* params, Int_t* error = 0) |
| virtual void | TObject::Execute(TMethod* method, TObjArray* params, Int_t* error = 0) |
| virtual void | TObject::ExecuteEvent(Int_t event, Int_t px, Int_t py) |
| virtual void | TObject::Fatal(const char* method, const char* msgfmt) const |
| virtual void | TNamed::FillBuffer(char*& buffer) |
| virtual TObject* | TObject::FindObject(const char* name) const |
| virtual TObject* | TObject::FindObject(const TObject* obj) const |
| void | FitAwmi(float* source) |
| void | FitStiefel(float* source) |
| Double_t* | GetAmplitudes() const |
| Double_t* | GetAmplitudesErrors() const |
| Double_t* | GetAreas() const |
| Double_t* | GetAreasErrors() const |
| void | GetBackgroundParameters(Double_t& a0, Double_t& a0Err, Double_t& a1, Double_t& a1Err, Double_t& a2, Double_t& a2Err) |
| Double_t | GetChi() const |
| virtual Option_t* | TObject::GetDrawOption() const |
| static Long_t | TObject::GetDtorOnly() |
| virtual const char* | TObject::GetIconName() const |
| virtual const char* | TNamed::GetName() const |
| virtual char* | TObject::GetObjectInfo(Int_t px, Int_t py) const |
| static Bool_t | TObject::GetObjectStat() |
| virtual Option_t* | TObject::GetOption() const |
| Double_t* | GetPositions() const |
| Double_t* | GetPositionsErrors() const |
| void | GetSigma(Double_t& sigma, Double_t& sigmaErr) |
| void | GetTailParameters(Double_t& t, Double_t& tErr, Double_t& b, Double_t& bErr, Double_t& s, Double_t& sErr) |
| virtual const char* | TNamed::GetTitle() const |
| virtual UInt_t | TObject::GetUniqueID() const |
| virtual Bool_t | TObject::HandleTimer(TTimer* timer) |
| virtual ULong_t | TNamed::Hash() const |
| virtual void | TObject::Info(const char* method, const char* msgfmt) const |
| virtual Bool_t | TObject::InheritsFrom(const char* classname) const |
| virtual Bool_t | TObject::InheritsFrom(const TClass* cl) const |
| virtual void | TObject::Inspect() const |
| void | TObject::InvertBit(UInt_t f) |
| virtual TClass* | IsA() const |
| virtual Bool_t | TObject::IsEqual(const TObject* obj) const |
| virtual Bool_t | TObject::IsFolder() const |
| Bool_t | TObject::IsOnHeap() const |
| virtual Bool_t | TNamed::IsSortable() const |
| Bool_t | TObject::IsZombie() const |
| virtual void | TNamed::ls(Option_t* option = "") const |
| void | TObject::MayNotUse(const char* method) const |
| virtual Bool_t | TObject::Notify() |
| static void | TObject::operator delete(void* ptr) |
| static void | TObject::operator delete(void* ptr, void* vp) |
| static void | TObject::operator delete[](void* ptr) |
| static void | TObject::operator delete[](void* ptr, void* vp) |
| void* | TObject::operator new(size_t sz) |
| void* | TObject::operator new(size_t sz, void* vp) |
| void* | TObject::operator new[](size_t sz) |
| void* | TObject::operator new[](size_t sz, void* vp) |
| TSpectrumFit& | operator=(const TSpectrumFit&) |
| virtual void | TObject::Paint(Option_t* option = "") |
| virtual void | TObject::Pop() |
| virtual void | TNamed::Print(Option_t* option = "") const |
| virtual Int_t | TObject::Read(const char* name) |
| virtual void | TObject::RecursiveRemove(TObject* obj) |
| void | TObject::ResetBit(UInt_t f) |
| virtual void | TObject::SaveAs(const char* filename = "", Option_t* option = "") const |
| virtual void | TObject::SavePrimitive(ostream& out, Option_t* option = "") |
| void | SetBackgroundParameters(Double_t a0Init, Bool_t fixA0, Double_t a1Init, Bool_t fixA1, Double_t a2Init, Bool_t fixA2) |
| void | TObject::SetBit(UInt_t f) |
| void | TObject::SetBit(UInt_t f, Bool_t set) |
| virtual void | TObject::SetDrawOption(Option_t* option = "") |
| static void | TObject::SetDtorOnly(void* obj) |
| void | SetFitParameters(Int_t xmin, Int_t xmax, Int_t numberIterations, Double_t alpha, Int_t statisticType, Int_t alphaOptim, Int_t power, Int_t fitTaylor) |
| virtual void | TNamed::SetName(const char* name) |
| virtual void | TNamed::SetNameTitle(const char* name, const char* title) |
| static void | TObject::SetObjectStat(Bool_t stat) |
| void | SetPeakParameters(Double_t sigma, Bool_t fixSigma, const Float_t* positionInit, const Bool_t* fixPosition, const Float_t* ampInit, const Bool_t* fixAmp) |
| void | SetTailParameters(Double_t tInit, Bool_t fixT, Double_t bInit, Bool_t fixB, Double_t sInit, Bool_t fixS) |
| virtual void | TNamed::SetTitle(const char* title = "") |
| virtual void | TObject::SetUniqueID(UInt_t uid) |
| virtual void | ShowMembers(TMemberInspector& insp, char* parent) |
| virtual Int_t | TNamed::Sizeof() const |
| virtual void | Streamer(TBuffer& b) |
| void | StreamerNVirtual(TBuffer& b) |
| virtual void | TObject::SysError(const char* method, const char* msgfmt) const |
| Bool_t | TObject::TestBit(UInt_t f) const |
| Int_t | TObject::TestBits(UInt_t f) const |
| virtual void | TObject::UseCurrentStyle() |
| virtual void | TObject::Warning(const char* method, const char* msgfmt) const |
| virtual Int_t | TObject::Write(const char* name = "0", Int_t option = 0, Int_t bufsize = 0) |
| virtual Int_t | TObject::Write(const char* name = "0", Int_t option = 0, Int_t bufsize = 0) const |
| enum { | kFitOptimChiCounts | |
| kFitOptimChiFuncValues | ||
| kFitOptimMaxLikelihood | ||
| kFitAlphaHalving | ||
| kFitAlphaOptimal | ||
| kFitPower2 | ||
| kFitPower4 | ||
| kFitPower6 | ||
| kFitPower8 | ||
| kFitPower10 | ||
| kFitPower12 | ||
| kFitTaylorOrderFirst | ||
| kFitTaylorOrderSecond | ||
| kFitNumRegulCycles | ||
| }; | ||
| enum TObject::EStatusBits { | kCanDelete | |
| kMustCleanup | ||
| kObjInCanvas | ||
| kIsReferenced | ||
| kHasUUID | ||
| kCannotPick | ||
| kNoContextMenu | ||
| kInvalidObject | ||
| }; | ||
| enum TObject::[unnamed] { | kIsOnHeap | |
| kNotDeleted | ||
| kZombie | ||
| kBitMask | ||
| kSingleKey | ||
| kOverwrite | ||
| kWriteDelete | ||
| }; |
| Int_t | fNPeaks | number of peaks present in fit, input parameter, it should be > 0 |
| Int_t | fNumberIterations | number of iterations in fitting procedure, input parameter, it should be > 0 |
| Int_t | fXmin | first fitted channel |
| Int_t | fXmax | last fitted channel |
| Int_t | fStatisticType | type of statistics, possible values kFitOptimChiCounts (chi square statistics with counts as weighting coefficients), kFitOptimChiFuncValues (chi square statistics with function values as weighting coefficients),kFitOptimMaxLikelihood |
| Int_t | fAlphaOptim | optimization of convergence algorithm, possible values kFitAlphaHalving, kFitAlphaOptimal |
| Int_t | fPower | possible values kFitPower2,4,6,8,10,12, for details see references. It applies only for Awmi fitting function. |
| Int_t | fFitTaylor | order of Taylor expansion, possible values kFitTaylorOrderFirst, kFitTaylorOrderSecond. It applies only for Awmi fitting function. |
| Double_t | fAlpha | convergence coefficient, input parameter, it should be positive number and <=1, for details see references |
| Double_t | fChi | here the fitting functions return resulting chi square |
| Double_t* | fPositionInit | [fNPeaks] array of initial values of peaks positions, input parameters |
| Double_t* | fPositionCalc | [fNPeaks] array of calculated values of fitted positions, output parameters |
| Double_t* | fPositionErr | [fNPeaks] array of position errors |
| Double_t* | fAmpInit | [fNPeaks] array of initial values of peaks amplitudes, input parameters |
| Double_t* | fAmpCalc | [fNPeaks] array of calculated values of fitted amplitudes, output parameters |
| Double_t* | fAmpErr | [fNPeaks] array of amplitude errors |
| Double_t* | fArea | [fNPeaks] array of calculated areas of peaks |
| Double_t* | fAreaErr | [fNPeaks] array of errors of peak areas |
| Double_t | fSigmaInit | initial value of sigma parameter |
| Double_t | fSigmaCalc | calculated value of sigma parameter |
| Double_t | fSigmaErr | error value of sigma parameter |
| Double_t | fTInit | initial value of t parameter (relative amplitude of tail), for details see html manual and references |
| Double_t | fTCalc | calculated value of t parameter |
| Double_t | fTErr | error value of t parameter |
| Double_t | fBInit | initial value of b parameter (slope), for details see html manual and references |
| Double_t | fBCalc | calculated value of b parameter |
| Double_t | fBErr | error value of b parameter |
| Double_t | fSInit | initial value of s parameter (relative amplitude of step), for details see html manual and references |
| Double_t | fSCalc | calculated value of s parameter |
| Double_t | fSErr | error value of s parameter |
| Double_t | fA0Init | initial value of background a0 parameter(backgroud is estimated as a0+a1*x+a2*x*x) |
| Double_t | fA0Calc | calculated value of background a0 parameter |
| Double_t | fA0Err | error value of background a0 parameter |
| Double_t | fA1Init | initial value of background a1 parameter(backgroud is estimated as a0+a1*x+a2*x*x) |
| Double_t | fA1Calc | calculated value of background a1 parameter |
| Double_t | fA1Err | error value of background a1 parameter |
| Double_t | fA2Init | initial value of background a2 parameter(backgroud is estimated as a0+a1*x+a2*x*x) |
| Double_t | fA2Calc | calculated value of background a2 parameter |
| Double_t | fA2Err | error value of background a2 parameter |
| Bool_t* | fFixPosition | [fNPeaks] array of logical values which allow to fix appropriate positions (not fit). However they are present in the estimated functional |
| Bool_t* | fFixAmp | [fNPeaks] array of logical values which allow to fix appropriate amplitudes (not fit). However they are present in the estimated functional |
| Bool_t | fFixSigma | logical value of sigma parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit). |
| Bool_t | fFixT | logical value of t parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit). |
| Bool_t | fFixB | logical value of b parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit). |
| Bool_t | fFixS | logical value of s parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit). |
| Bool_t | fFixA0 | logical value of a0 parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit). |
| Bool_t | fFixA1 | logical value of a1 parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit). |
| Bool_t | fFixA2 | logical value of a2 parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit). |
| TString | TNamed::fName | object identifier |
| TString | TNamed::fTitle | object title |
THIS CLASS CONTAINS ADVANCED SPECTRA FITTING FUNCTIONS.
These functions were written by:
Miroslav Morhac
Institute of Physics
Slovak Academy of Sciences
Dubravska cesta 9, 842 28 BRATISLAVA
SLOVAKIA
email:fyzimiro@savba.sk, fax:+421 7 54772479
The original code in C has been repackaged as a C++ class by R.Brun
The algorithms in this class have been published in the following
references:
[1] M. Morhac et al.: Efficient fitting algorithms applied to
analysis of coincidence gamma-ray spectra. Computer Physics
Communications, Vol 172/1 (2005) pp. 19-41.
[2] M. Morhac et al.: Study of fitting algorithms applied to
simultaneous analysis of large number of peaks in gamma-ray spectra.
Applied Spectroscopy, Vol. 57, No. 7, pp. 753-760, 2003.
____________________________________________________________________________
numberPeaks: number of fitted peaks (must be greater than zero) the constructor allocates arrays for all fitted parameters (peak positions, amplitudes etc) and sets the member variables to their default values. One can change these variables by member functions (setters) of TSpectrumFit class.
Shape function of the fitted peaks is
 |
where a represents vector of fitted parameters (positions p(j), amplitudes A(j), sigma, relative amplitudes T, S and slope B).
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of error function of x.
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of peak shape function (see manual)
according to amplitude of peak.
Function parameters:
-i-channel
-i0-position of peak
-sigma-sigma of peak
-t, s-relative amplitudes
-b-slope
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of peak shape function (see manual)
according to peak position.
Function parameters:
-i-channel
-amp-amplitude of peak
-i0-position of peak
-sigma-sigma of peak
-t, s-relative amplitudes
-b-slope
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates second derivative of peak shape function
(see manual) according to peak position.
Function parameters:
-i-channel
-amp-amplitude of peak
-i0-position of peak
-sigma-width of peak
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of peaks shape function (see manual)
according to sigma of peaks.
Function parameters:
-num_of_fitted_peaks-number of fitted peaks
-i-channel
-parameter-array of peaks parameters (amplitudes and positions)
-sigma-sigma of peak
-t, s-relative amplitudes
-b-slope
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates second derivative of peaks shape function
(see manual) according to sigma of peaks.
Function parameters:
-num_of_fitted_peaks-number of fitted peaks
-i-channel
-parameter-array of peaks parameters (amplitudes and positions)
-sigma-sigma of peak
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of peaks shape function (see manual)
according to relative amplitude t.
Function parameters:
-num_of_fitted_peaks-number of fitted peaks
-i-channel
-parameter-array of peaks parameters (amplitudes and positions)
-sigma-sigma of peak
-b-slope
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of peaks shape function (see manual)
according to relative amplitude s.
Function parameters:
-num_of_fitted_peaks-number of fitted peaks
-i-channel
-parameter-array of peaks parameters (amplitudes and positions)
-sigma-sigma of peak
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of peaks shape function (see manual)
according to slope b.
Function parameters:
-num_of_fitted_peaks-number of fitted peaks
-i-channel
-parameter-array of peaks parameters (amplitudes and positions)
-sigma-sigma of peak
-t-relative amplitude
-b-slope
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates peaks shape function (see manual)
Function parameters:
-num_of_fitted_peaks-number of fitted peaks
-i-channel
-parameter-array of peaks parameters (amplitudes and positions)
-sigma-sigma of peak
-t, s-relative amplitudes
-b-slope
-a0, a1, a2- background coefficients
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates area of a peak
Function parameters:
-a-amplitude of the peak
-sigma-sigma of peak
-t-relative amplitude
-b-slope
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of the area of peak
according to its amplitude.
Function parameters:
-sigma-sigma of peak
-t-relative amplitudes
-b-slope
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of the area of peak
according to sigma of peaks.
Function parameters:
-a-amplitude of peak
-t-relative amplitudes
-b-slope
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of the area of peak
according to t parameter.
Function parameters:
-sigma-sigma of peak
-t-relative amplitudes
-b-slope
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates derivative of the area of peak
according to b parameter.
Function parameters:
-sigma-sigma of peak
-t-relative amplitudes
-b-slope
ONE-DIMENSIONAL FIT FUNCTION
ALGORITHM WITHOUT MATRIX INVERSION
This function fits the source spectrum. The calling program should
fill in input parameters of the TSpectrumFit class
The fitted parameters are written into
TSpectrumFit class output parameters and fitted data are written into
source spectrum.
Function parameters:
source-pointer to the vector of source spectrum
Fitting
Goal: to estimate simultaneously peak shape parameters in spectra with large number of peaks
peaks can be fitted separately, each peak (or multiplets) in a region or together all peaks in a spectrum. To fit separately each peak one needs to determine the fitted region. However it can happen that the regions of neighboring peaks are overlapping. Then the results of fitting are very poor. On the other hand, when fitting together all peaks found in a spectrum, one needs to have a method that is stable (converges) and fast enough to carry out fitting in reasonable time
we have implemented the nonsymmetrical semiempirical peak shape function [1]
it contains the symmetrical Gaussian as well as nonsymmetrical terms.
 |
where T and S are relative amplitudes and B is slope.
algorithm without matrix inversion (AWMI) allows fitting tens, hundreds of peaks simultaneously that represent sometimes thousands of parameters [2], [5].
Function:
void TSpectrumFit::FitAwmi(float *fSource)
This function fits the source spectrum using AWMI algorithm. The calling program should fill in input fitting parameters of the TSpectrumFit class using a set of TSpectrumFit setters. The fitted parameters are written into the class and the fitted data are written into source spectrum.
Parameter:
fSource-pointer to the vector of source spectrum
Member variables of the TSpectrumFit class:
Int_t fNPeaks; //number of peaks present in fit, input parameter, it should be > 0
Int_t fNumberIterations; //number of iterations in fitting procedure, input parameter, it should be > 0
Int_t fXmin; //first fitted channel
Int_t fXmax; //last fitted channel
Int_t fStatisticType; //type of statistics, possible values kFitOptimChiCounts (chi square statistics with counts as weighting coefficients), kFitOptimChiFuncValues (chi square statistics with function values as weighting coefficients),kFitOptimMaxLikelihood
Int_t fAlphaOptim; //optimization of convergence algorithm, possible values kFitAlphaHalving, kFitAlphaOptimal
Int_t fPower; //possible values kFitPower2,4,6,8,10,12, for details see references. It applies only for Awmi fitting function.
Int_t fFitTaylor; //order of Taylor expansion, possible values kFitTaylorOrderFirst, kFitTaylorOrderSecond. It applies only for Awmi fitting function.
Double_t fAlpha; //convergence coefficient, input parameter, it should be positive number and <=1, for details see references
Double_t fChi; //here the fitting functions return resulting chi square
Double_t *fPositionInit; //[fNPeaks] array of initial values of peaks positions, input parameters
Double_t *fPositionCalc; //[fNPeaks] array of calculated values of fitted positions, output parameters
Double_t *fPositionErr; //[fNPeaks] array of position errors
Double_t *fAmpInit; //[fNPeaks] array of initial values of peaks amplitudes, input parameters
Double_t *fAmpCalc; //[fNPeaks] array of calculated values of fitted amplitudes, output parameters
Double_t *fAmpErr; //[fNPeaks] array of amplitude errors
Double_t *fArea; //[fNPeaks] array of calculated areas of peaks
Double_t *fAreaErr; //[fNPeaks] array of errors of peak areas
Double_t fSigmaInit; //initial value of sigma parameter
Double_t fSigmaCalc; //calculated value of sigma parameter
Double_t fSigmaErr; //error value of sigma parameter
Double_t fTInit; //initial value of t parameter (relative amplitude of tail), for details see html manual and references
Double_t fTCalc; //calculated value of t parameter
Double_t fTErr; //error value of t parameter
Double_t fBInit; //initial value of b parameter (slope), for details see html manual and references
Double_t fBCalc; //calculated value of b parameter
Double_t fBErr; //error value of b parameter
Double_t fSInit; //initial value of s parameter (relative amplitude of step), for details see html manual and references
Double_t fSCalc; //calculated value of s parameter
Double_t fSErr; //error value of s parameter
Double_t fA0Init; //initial value of background a0 parameter(backgroud is estimated as a0+a1*x+a2*x*x)
Double_t fA0Calc; //calculated value of background a0 parameter
Double_t fA0Err; //error value of background a0 parameter
Double_t fA1Init; //initial value of background a1 parameter(backgroud is estimated as a0+a1*x+a2*x*x)
Double_t fA1Calc; //calculated value of background a1 parameter
Double_t fA1Err; //error value of background a1 parameter
Double_t fA2Init; //initial value of background a2 parameter(backgroud is estimated as a0+a1*x+a2*x*x)
Double_t fA2Calc; //calculated value of background a2 parameter
Double_t fA2Err; //error value of background a2 parameter
Bool_t *fFixPosition; //[fNPeaks] array of logical values which allow to fix appropriate positions (not fit). However they are present in the estimated functional
Bool_t *fFixAmp; //[fNPeaks] array of logical values which allow to fix appropriate amplitudes (not fit). However they are present in the estimated functional
Bool_t fFixSigma; //logical value of sigma parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit).
Bool_t fFixT; //logical value of t parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit).
Bool_t fFixB; //logical value of b parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit).
Bool_t fFixS; //logical value of s parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit).
Bool_t fFixA0; //logical value of a0 parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit).
Bool_t fFixA1; //logical value of a1 parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit).
Bool_t fFixA2; //logical value of a2 parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit).
References:
[1] Phillps G.W., Marlow K.W., NIM 137 (1976) 525.
[2] I. A. Slavic: Nonlinear least-squares fitting without matrix inversion applied to complex Gaussian spectra analysis. NIM 134 (1976) 285-289.
[3] T. Awaya: A new method for curve fitting to the data with low statistics not using chi-square method. NIM 165 (1979) 317-323.
[4] T. Hauschild, M. Jentschel: Comparison of maximum likelihood estimation and chi-square statistics applied to counting experiments. NIM A 457 (2001) 384-401.
[5] M. Morháč, J. Kliman, M. Jandel, Ľ. Krupa, V. Matouek: Study of fitting algorithms applied to simultaneous analysis of large number of peaks in -ray spectra. Applied Spectroscopy, Vol. 57, No. 7, pp. 753-760, 2003
Example script FitAwmi.c:

Fig. 1 Original spectrum (black line) and fitted spectrum using AWMI algorithm (red line) and number of iteration steps = 1000. Positions of fitted peaks are denoted by markers
Script:
// Example to illustrate fitting function using AWMI algorithm.
// To execute this example, do
// root > .x FitAwmi.C
void FitAwmi() {
Double_t a;
Int_t i,nfound=0,bin;
Int_t nbins = 256;
Int_t xmin = 0;
Int_t xmax = nbins;
Float_t * source = new float[nbins];
Float_t * dest = new float[nbins];
TH1F *h = new TH1F("h","Fitting using AWMI algorithm",nbins,xmin,xmax);
TH1F *d = new TH1F("d","",nbins,xmin,xmax);
TFile *f = new TFile("TSpectrum.root");
h=(TH1F*) f->Get("fit;1");
for (i = 0; i < nbins; i++) source[i]=h->GetBinContent(i + 1);
TCanvas *Fit1 = gROOT->GetListOfCanvases()->FindObject("Fit1");
if (!Fit1) Fit1 = new TCanvas("Fit1","Fit1",10,10,1000,700);
h->Draw("L");
TSpectrum *s = new TSpectrum();
//searching for candidate peaks positions
nfound = s->SearchHighRes(source, dest, nbins, 2, 0.1, kFALSE, 10000, kFALSE, 0);
Bool_t *FixPos = new Bool_t[nfound];
Bool_t *FixAmp = new Bool_t[nfound];
for(i = 0; i< nfound ; i++){
FixPos[i] = kFALSE;
FixAmp[i] = kFALSE;
}
//filling in the initial estimates of the input parameters
Float_t *PosX = new Float_t[nfound];
Float_t *PosY = new Float_t[nfound];
PosX = s->GetPositionX();
for (i = 0; i < nfound; i++) {
a=PosX[i];
bin = 1 + Int_t(a + 0.5);
PosY[i] = h->GetBinContent(bin);
}
TSpectrumFit *pfit=new TSpectrumFit(nfound);
pfit->SetFitParameters(xmin, xmax-1, 1000, 0.1, pfit->kFitOptimChiCounts, pfit->kFitAlphaHalving, pfit->kFitPower2, pfit->kFitTaylorOrderFirst);
pfit->SetPeakParameters(2, kFALSE, PosX, (Bool_t *) FixPos, PosY, (Bool_t *) FixAmp);
pfit->FitAwmi(source);
Double_t *CalcPositions = new Double_t[nfound];
Double_t *CalcAmplitudes = new Double_t[nfound];
CalcPositions=pfit->GetPositions();
CalcAmplitudes=pfit->GetAmplitudes();
for (i = 0; i < nbins; i++) d->SetBinContent(i + 1,source[i]);
d->SetLineColor(kRed);
d->Draw("SAME L");
for (i = 0; i < nfound; i++) {
a=CalcPositions[i];
bin = 1 + Int_t(a + 0.5);
PosX[i] = d->GetBinCenter(bin);
PosY[i] = d->GetBinContent(bin);
}
TPolyMarker * pm = (TPolyMarker*)h->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject("TPolyMarker");
if (pm) {
h->GetListOfFunctions()->Remove(pm);
delete pm;
}
pm = new TPolyMarker(nfound, PosX, PosY);
h->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(pm);
pm->SetMarkerStyle(23);
pm->SetMarkerColor(kRed);
pm->SetMarkerSize(1);
}
AUXILIARY FUNCTION
This function calculates solution of the system of linear equations.
The matrix a should have a dimension size*(size+4)
The calling function should fill in the matrix, the column size should
contain vector y (right side of the system of equations). The result is
placed into size+1 column of the matrix.
according to sigma of peaks.
Function parameters:
-a-matrix with dimension size*(size+4) //
-size-number of rows of the matrix
ONE-DIMENSIONAL FIT FUNCTION
ALGORITHM WITH MATRIX INVERSION (STIEFEL-HESTENS METHOD)
This function fits the source spectrum. The calling program should
fill in input parameters
The fitted parameters are written into
output parameters and fitted data are written into
source spectrum.
Function parameters:
source-pointer to the vector of source spectrum
Stiefel fitting algorithm
Function:
void TSpectrumFit::FitStiefel(float *fSource)
This function fits the source spectrum using Stiefel-Hestens method [1] (see Awmi function). The calling program should fill in input fitting parameters of the TSpectrumFit class using a set of TSpectrumFit setters. The fitted parameters are written into the class and the fitted data are written into source spectrum. It converges faster than Awmi method.
Parameter:
fSource-pointer to the vector of source spectrum
Example script FitStiefel.c:
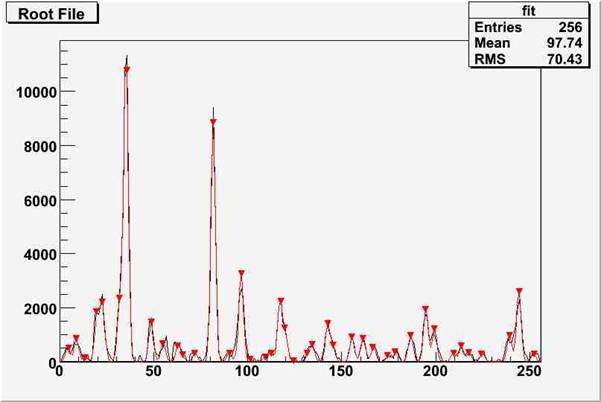
Fig. 2 Original spectrum (black line) and fitted spectrum using Stiefel-Hestens method (red line) and number of iteration steps = 100. Positions of fitted peaks are denoted by markers
Script:
// Example to illustrate fitting function using Stiefel-Hestens method.
// To execute this example, do
// root > .x FitStiefel.C
void FitStiefel() {
Double_t a;
Int_t i,nfound=0,bin;
Int_t nbins = 256;
Int_t xmin = 0;
Int_t xmax = nbins;
Float_t * source = new float[nbins];
Float_t * dest = new float[nbins];
TH1F *h = new TH1F("h","Fitting using AWMI algorithm",nbins,xmin,xmax);
TH1F *d = new TH1F("d","",nbins,xmin,xmax);
TFile *f = new TFile("TSpectrum.root");
h=(TH1F*) f->Get("fit;1");
for (i = 0; i < nbins; i++) source[i]=h->GetBinContent(i + 1);
TCanvas *Fit1 = gROOT->GetListOfCanvases()->FindObject("Fit1");
if (!Fit1) Fit1 = new TCanvas("Fit1","Fit1",10,10,1000,700);
h->Draw("L");
TSpectrum *s = new TSpectrum();
//searching for candidate peaks positions
nfound = s->SearchHighRes(source, dest, nbins, 2, 0.1, kFALSE, 10000, kFALSE, 0);
Bool_t *FixPos = new Bool_t[nfound];
Bool_t *FixAmp = new Bool_t[nfound];
for(i = 0; i< nfound ; i++){
FixPos[i] = kFALSE;
FixAmp[i] = kFALSE;
}
//filling in the initial estimates of the input parameters
Float_t *PosX = new Float_t[nfound];
Float_t *PosY = new Float_t[nfound];
PosX = s->GetPositionX();
for (i = 0; i < nfound; i++) {
a=PosX[i];
bin = 1 + Int_t(a + 0.5);
PosY[i] = h->GetBinContent(bin);
}
TSpectrumFit *pfit=new TSpectrumFit(nfound);
pfit->SetFitParameters(xmin, xmax-1, 1000, 0.1, pfit->kFitOptimChiCounts, pfit->kFitAlphaHalving, pfit->kFitPower2, pfit->kFitTaylorOrderFirst);
pfit->SetPeakParameters(2, kFALSE, PosX, (Bool_t *) FixPos, PosY, (Bool_t *) FixAmp);
pfit->FitStiefel(source);
Double_t *CalcPositions = new Double_t[nfound];
Double_t *CalcAmplitudes = new Double_t[nfound];
CalcPositions=pfit->GetPositions();
CalcAmplitudes=pfit->GetAmplitudes();
for (i = 0; i < nbins; i++) d->SetBinContent(i + 1,source[i]);
d->SetLineColor(kRed);
d->Draw("SAME L");
for (i = 0; i < nfound; i++) {
a=CalcPositions[i];
bin = 1 + Int_t(a + 0.5);
PosX[i] = d->GetBinCenter(bin);
PosY[i] = d->GetBinContent(bin);
}
TPolyMarker * pm = (TPolyMarker*)h->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject("TPolyMarker");
if (pm) {
h->GetListOfFunctions()->Remove(pm);
delete pm;
}
pm = new TPolyMarker(nfound, PosX, PosY);
h->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(pm);
pm->SetMarkerStyle(23);
pm->SetMarkerColor(kRed);
pm->SetMarkerSize(1);
}
SETTER FUNCTION
This function sets the following fitting parameters:
-xmin, xmax - fitting region
-numberIterations - # of desired iterations in the fit
-alpha - convergence coefficient, it should be positive number and <=1, for details see references
-statisticType - type of statistics, possible values kFitOptimChiCounts (chi square statistics with counts as weighting coefficients), kFitOptimChiFuncValues (chi square statistics with function values as weighting coefficients),kFitOptimMaxLikelihood
-alphaOptim - optimization of convergence algorithm, possible values kFitAlphaHalving, kFitAlphaOptimal
-power - possible values kFitPower2,4,6,8,10,12, for details see references. It applies only for Awmi fitting function.
-fitTaylor - order of Taylor expansion, possible values kFitTaylorOrderFirst, kFitTaylorOrderSecond. It applies only for Awmi fitting function.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
SETTER FUNCTION
This function sets the following fitting parameters of peaks:
-sigma - initial value of sigma parameter
-fixSigma - logical value of sigma parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit)
-positionInit - aray of initial values of peaks positions
-fixPosition - array of logical values which allow to fix appropriate positions (not fit). However they are present in the estimated functional.
-ampInit - aray of initial values of peaks amplitudes
-fixAmp - aray of logical values which allow to fix appropriate amplitudes (not fit). However they are present in the estimated functional
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
SETTER FUNCTION
This function sets the following fitting parameters of background:
-a0Init - initial value of a0 parameter (backgroud is estimated as a0+a1*x+a2*x*x)
-fixA0 - logical value of a0 parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit)
-a1Init - initial value of a1 parameter
-fixA1 - logical value of a1 parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit)
-a2Init - initial value of a2 parameter
-fixA2 - logical value of a2 parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit)
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
SETTER FUNCTION
This function sets the following fitting parameters of tails of peaks
-tInit - initial value of t parameter
-fixT - logical value of t parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit)
-bInit - initial value of b parameter
-fixB - logical value of b parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit)
-sInit - initial value of s parameter
-fixS - logical value of s parameter, which allows to fix the parameter (not to fit)
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
GETTER FUNCTION
This function gets the sigma parameter and its error
-sigma - gets the fitted value of sigma parameter
-sigmaErr - gets error value of sigma parameter
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
GETTER FUNCTION
This function gets the background parameters and their errors
-a0 - gets the fitted value of a0 parameter
-a0Err - gets error value of a0 parameter
-a1 - gets the fitted value of a1 parameter
-a1Err - gets error value of a1 parameter
-a2 - gets the fitted value of a2 parameter
-a2Err - gets error value of a2 parameter
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
GETTER FUNCTION
This function gets the tail parameters and their errors
-t - gets the fitted value of t parameter
-tErr - gets error value of t parameter
-b - gets the fitted value of b parameter
-bErr - gets error value of b parameter
-s - gets the fitted value of s parameter
-sErr - gets error value of s parameter
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////