Implementing VirtualIntegratorOneDim Interface
Return Integral of function between a and b.
Based on original CERNLIB routine DGAUSS by Sigfried Kolbig
converted to C++ by Rene Brun
This function computes, to an attempted specified accuracy, the value
of the integral.
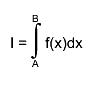 Usage:
In any arithmetic expression, this function has the approximate value
of the integral I.
- A, B: End-points of integration interval. Note that B may be less
than A.
- params: Array of function parameters. If 0, use current parameters.
- epsilon: Accuracy parameter (see Accuracy).
Method:
For any interval [a,b] we define g8(a,b) and g16(a,b) to be the 8-point
and 16-point Gaussian quadrature approximations to
Usage:
In any arithmetic expression, this function has the approximate value
of the integral I.
- A, B: End-points of integration interval. Note that B may be less
than A.
- params: Array of function parameters. If 0, use current parameters.
- epsilon: Accuracy parameter (see Accuracy).
Method:
For any interval [a,b] we define g8(a,b) and g16(a,b) to be the 8-point
and 16-point Gaussian quadrature approximations to
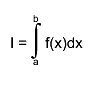 and define
and define
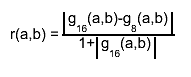 Then,
Then,
 where, starting with x0 = A and finishing with xk = B,
the subdivision points xi(i=1,2,...) are given by
where, starting with x0 = A and finishing with xk = B,
the subdivision points xi(i=1,2,...) are given by
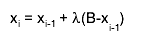
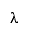 is equal to the first member of the
sequence 1,1/2,1/4,... for which r(xi-1, xi) < EPS.
If, at any stage in the process of subdivision, the ratio
is equal to the first member of the
sequence 1,1/2,1/4,... for which r(xi-1, xi) < EPS.
If, at any stage in the process of subdivision, the ratio
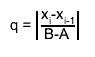 is so small that 1+0.005q is indistinguishable from 1 to
machine accuracy, an error exit occurs with the function value
set equal to zero.
Accuracy:
Unless there is severe cancellation of positive and negative values of
f(x) over the interval [A,B], the relative error may be considered as
specifying a bound on the <I>relative</I> error of I in the case
|I|>1, and a bound on the absolute error in the case |I|<1. More
precisely, if k is the number of sub-intervals contributing to the
approximation (see Method), and if
is so small that 1+0.005q is indistinguishable from 1 to
machine accuracy, an error exit occurs with the function value
set equal to zero.
Accuracy:
Unless there is severe cancellation of positive and negative values of
f(x) over the interval [A,B], the relative error may be considered as
specifying a bound on the <I>relative</I> error of I in the case
|I|>1, and a bound on the absolute error in the case |I|<1. More
precisely, if k is the number of sub-intervals contributing to the
approximation (see Method), and if
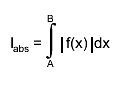 then the relation
then the relation
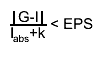 will nearly always be true, provided the routine terminates without
printing an error message. For functions f having no singularities in
the closed interval [A,B] the accuracy will usually be much higher than
this.
Error handling:
The requested accuracy cannot be obtained (see Method).
The function value is set equal to zero.
Note 1:
Values of the function f(x) at the interval end-points A and B are not
required. The subprogram may therefore be used when these values are
undefined.
will nearly always be true, provided the routine terminates without
printing an error message. For functions f having no singularities in
the closed interval [A,B] the accuracy will usually be much higher than
this.
Error handling:
The requested accuracy cannot be obtained (see Method).
The function value is set equal to zero.
Note 1:
Values of the function f(x) at the interval end-points A and B are not
required. The subprogram may therefore be used when these values are
undefined.


Usage: In any arithmetic expression, this function has the approximate value of the integral I. - A, B: End-points of integration interval. Note that B may be less than A. - params: Array of function parameters. If 0, use current parameters. - epsilon: Accuracy parameter (see Accuracy). Method: For any interval [a,b] we define g8(a,b) and g16(a,b) to be the 8-point and 16-point Gaussian quadrature approximations to
and define
Then,
where, starting with x0 = A and finishing with xk = B, the subdivision points xi(i=1,2,...) are given by
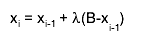
is equal to the first member of the sequence 1,1/2,1/4,... for which r(xi-1, xi) < EPS. If, at any stage in the process of subdivision, the ratio
is so small that 1+0.005q is indistinguishable from 1 to machine accuracy, an error exit occurs with the function value set equal to zero. Accuracy: Unless there is severe cancellation of positive and negative values of f(x) over the interval [A,B], the relative error may be considered as specifying a bound on the <I>relative</I> error of I in the case |I|>1, and a bound on the absolute error in the case |I|<1. More precisely, if k is the number of sub-intervals contributing to the approximation (see Method), and if
then the relation
will nearly always be true, provided the routine terminates without printing an error message. For functions f having no singularities in the closed interval [A,B] the accuracy will usually be much higher than this. Error handling: The requested accuracy cannot be obtained (see Method). The function value is set equal to zero. Note 1: Values of the function f(x) at the interval end-points A and B are not required. The subprogram may therefore be used when these values are undefined.