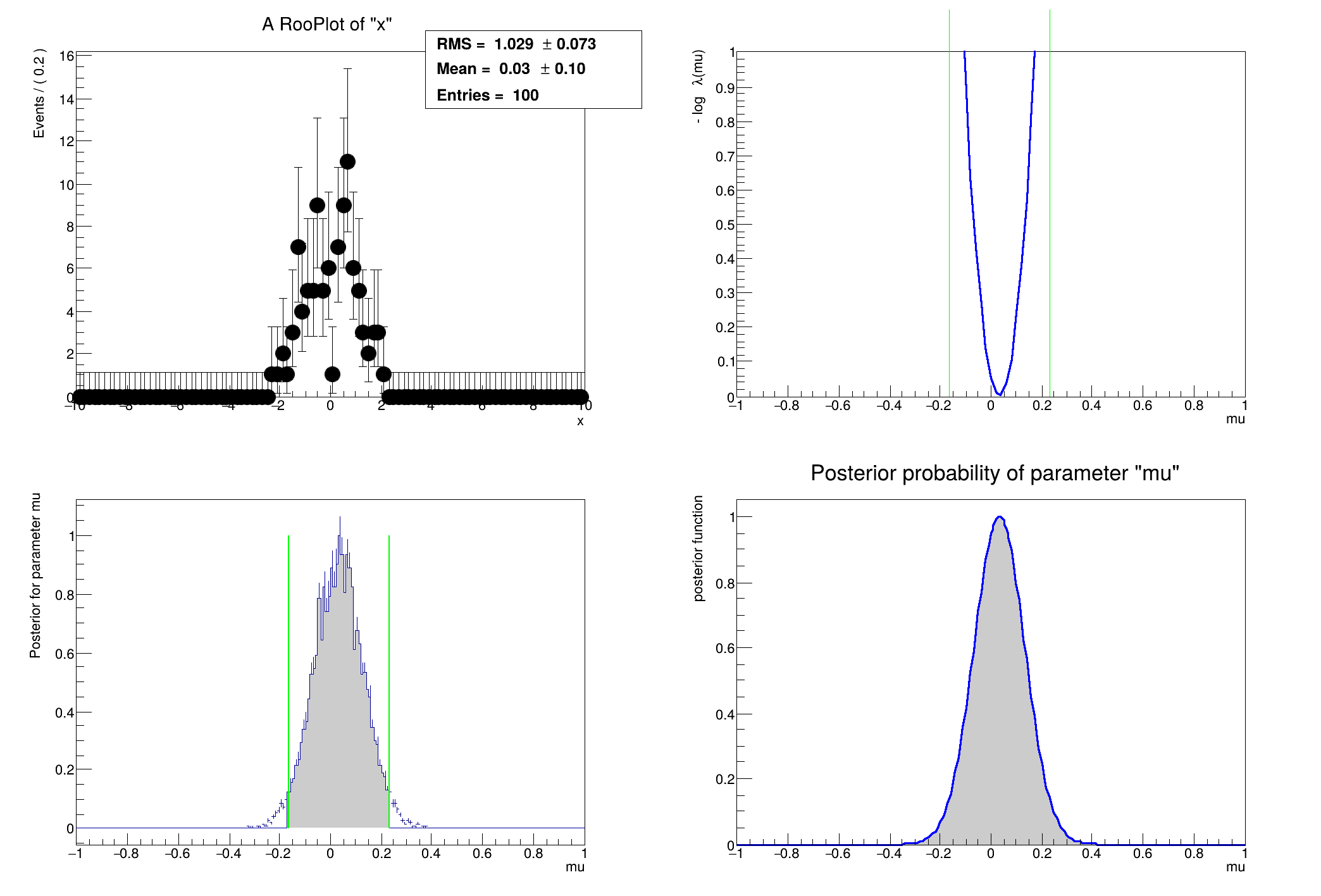
An example that shows confidence intervals with four techniques. The model is a Normal Gaussian G(x|mu,sigma) with 100 samples of x. The answer is known analytically, so this is a good example to validate the RooStats tools.
[#0] WARNING:InputArguments -- The parameter 'sigma' with range [-inf, inf] of the RooGaussian 'normal' exceeds the safe range of (0, inf). Advise to limit its range.
RooDataSet::normalData[x] = 100 entries
[#1] INFO:InputArguments -- The deprecated RooFit::CloneData(1) option passed to createNLL() is ignored.
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAbsPdf::fitTo(normal_over_normal_Int[x]) fixing normalization set for coefficient determination to observables in data
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- using generic CPU library compiled with no vectorizations
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- Creation of NLL object took 7.02836 ms
[#0] PROGRESS:Minimization -- ProfileLikelihoodCalcultor::DoGLobalFit - find MLE
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAddition::defaultErrorLevel(nll_normal_over_normal_Int[x]_normalData) Summation contains a RooNLLVar, using its error level
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooAbsMinimizerFcn::setOptimizeConst: activating const optimization
[#0] PROGRESS:Minimization -- ProfileLikelihoodCalcultor::DoMinimizeNLL - using Minuit2 / with strategy 1
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
[#1] INFO:Minimization --
RooFitResult: minimized FCN value: 144.292, estimated distance to minimum: 1.8174e-09
covariance matrix quality: Full, accurate covariance matrix
Status : MINIMIZE=0
Floating Parameter FinalValue +/- Error
-------------------- --------------------------
mu 3.3073e-02 +/- 9.98e-02
=== Using the following for Example G(x|mu,1) ===
Observables: RooArgSet:: = (x)
Parameters of Interest: RooArgSet:: = (mu)
PDF: RooGaussian::normal[ x=x mean=mu sigma=sigma ] = 0.999453
FeldmanCousins: ntoys per point: adaptive
FeldmanCousins: nEvents per toy will not fluctuate, will always be 100
FeldmanCousins: Model has no nuisance parameters
FeldmanCousins: # points to test = 100
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 1/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 52.3345
mu=-0.99 [-inf, 1.44394] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 2/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 50.3084
mu=-0.97 [-inf, 1.79333] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 3/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 48.3222
mu=-0.95 [-inf, 2.15157] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 4/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 46.3758
mu=-0.93 [-inf, 1.35751] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 5/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 44.4699
mu=-0.91 [-inf, 3.34994] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 6/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 42.6037
mu=-0.89 [-inf, 2.51372] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 7/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 40.7776
mu=-0.87 [-inf, 2.23515] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 8/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 38.9914
mu=-0.85 [-inf, 1.58856] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 9/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 37.2453
mu=-0.83 [-inf, 1.815] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 10/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 35.5391
mu=-0.81 [-inf, 2.60213] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 11/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 33.873
mu=-0.79 [-inf, 1.83579] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 12/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 32.2468
mu=-0.77 [-inf, 1.80677] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 13/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 30.6606
mu=-0.75 [-inf, 2.46798] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 14/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 29.1145
mu=-0.73 [-inf, 1.76469] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 15/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 27.6083
mu=-0.71 [-inf, 2.10923] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 16/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 26.1422
mu=-0.69 [-inf, 1.96364] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 17/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 24.716
mu=-0.67 [-inf, 2.46737] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 18/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 23.3298
mu=-0.65 [-inf, 2.22208] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 19/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 21.9837
mu=-0.63 [-inf, 1.92004] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 20/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 20.6774
mu=-0.61 [-inf, 2.09449] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 21/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 19.4114
mu=-0.59 [-inf, 2.82549] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 22/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 18.1852
mu=-0.57 [-inf, 2.44483] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 23/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 16.9991
mu=-0.55 [-inf, 1.47648] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 24/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 15.8529
mu=-0.53 [-inf, 1.64253] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 25/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 14.7467
mu=-0.51 [-inf, 3.23375] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 26/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 13.6806
mu=-0.49 [-inf, 1.36352] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 27/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 12.6544
mu=-0.47 [-inf, 2.24046] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 28/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 11.6683
mu=-0.45 [-inf, 1.99249] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 29/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 10.7221
mu=-0.43 [-inf, 2.54633] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 30/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 9.81595
mu=-0.41 [-inf, 2.19145] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 31/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 8.94979
mu=-0.39 [-inf, 2.25083] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 32/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 8.12363
mu=-0.37 [-inf, 2.63436] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 33/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 7.33748
mu=-0.35 [-inf, 1.7752] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 34/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 6.59132
mu=-0.33 [-inf, 2.63173] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 35/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 5.88516
mu=-0.31 [-inf, 2.2561] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 36/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 5.219
mu=-0.29 [-inf, 2.0388] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 37/100 total MC = 234 this test stat = 4.59284
mu=-0.27 [-inf, 1.92574] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 38/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 4.00668
mu=-0.25 [-inf, 2.51905] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 39/100 total MC = 234 this test stat = 3.46053
mu=-0.23 [-inf, 2.20004] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 40/100 total MC = 234 this test stat = 2.95437
mu=-0.21 [-inf, 1.49924] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 41/100 total MC = 234 this test stat = 2.48821
mu=-0.19 [-inf, 1.88454] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 42/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 2.06205
mu=-0.17 [-inf, 2.92073] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 43/100 total MC = 234 this test stat = 1.6759
mu=-0.15 [-inf, 2.19199] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 44/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 1.32974
mu=-0.13 [-inf, 1.94832] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 45/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 1.02358
mu=-0.11 [-inf, 2.16863] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 46/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.757266
mu=-0.09 [-inf, 1.46141] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 47/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.531219
mu=-0.07 [-inf, 4.11006] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 48/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.345097
mu=-0.05 [-inf, 2.11338] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 49/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.198947
mu=-0.03 [-inf, 2.38127] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 50/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.09279
mu=-0.01 [-inf, 3.0189] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 51/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.026632
mu=0.01 [-inf, 2.23423] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 52/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.000474009
mu=0.03 [-inf, 2.54313] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 53/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.014316
mu=0.05 [-inf, 1.52484] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 54/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.0681571
mu=0.07 [-inf, 2.72021] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 55/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.161992
mu=0.09 [-inf, 3.26474] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 56/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.2958
mu=0.11 [-inf, 2.81134] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 57/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.469534
mu=0.13 [-inf, 2.59127] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 58/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.683526
mu=0.15 [-inf, 2.60194] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 59/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 0.937368
mu=0.17 [-inf, 1.94974] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 60/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 1.23121
mu=0.19 [-inf, 1.73838] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 61/100 total MC = 702 this test stat = 1.56505
mu=0.21 [-inf, 1.73023] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 62/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 1.93888
mu=0.23 [-inf, 3.06401] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 63/100 total MC = 234 this test stat = 2.35273
mu=0.25 [-inf, 1.63166] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 64/100 total MC = 234 this test stat = 2.80658
mu=0.27 [-inf, 1.83441] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 65/100 total MC = 234 this test stat = 3.30042
mu=0.29 [-inf, 2.06725] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 66/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 3.83426
mu=0.31 [-inf, 2.10484] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 67/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 4.4081
mu=0.33 [-inf, 2.1714] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 68/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 5.02195
mu=0.35 [-inf, 2.77418] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 69/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 5.67579
mu=0.37 [-inf, 2.39797] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 70/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 6.36963
mu=0.39 [-inf, 1.83585] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 71/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 7.10347
mu=0.41 [-inf, 1.92776] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 72/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 7.87731
mu=0.43 [-inf, 1.62512] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 73/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 8.69116
mu=0.45 [-inf, 1.5721] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 74/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 9.545
mu=0.47 [-inf, 1.9811] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 75/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 10.4388
mu=0.49 [-inf, 3.71619] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 76/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 11.3727
mu=0.51 [-inf, 2.09734] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 77/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 12.3465
mu=0.53 [-inf, 1.61789] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 78/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 13.3604
mu=0.55 [-inf, 1.75937] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 79/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 14.4142
mu=0.57 [-inf, 2.16051] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 80/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 15.5081
mu=0.59 [-inf, 2.48971] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 81/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 16.6419
mu=0.61 [-inf, 2.15114] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 82/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 17.8157
mu=0.63 [-inf, 2.63832] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 83/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 19.0296
mu=0.65 [-inf, 2.12006] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 84/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 20.2834
mu=0.67 [-inf, 1.70414] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 85/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 21.5773
mu=0.69 [-inf, 2.54958] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 86/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 22.9111
mu=0.71 [-inf, 2.27992] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 87/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 24.2849
mu=0.73 [-inf, 2.99068] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 88/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 25.6988
mu=0.75 [-inf, 1.60655] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 89/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 27.1526
mu=0.77 [-inf, 1.61728] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 90/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 28.6465
mu=0.79 [-inf, 1.92571] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 91/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 30.1803
mu=0.81 [-inf, 1.69221] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 92/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 31.7542
mu=0.83 [-inf, 3.26227] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 93/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 33.368
mu=0.85 [-inf, 1.75583] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 94/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 35.0218
mu=0.87 [-inf, 2.54103] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 95/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 36.7157
mu=0.89 [-inf, 2.267] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 96/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 38.4495
mu=0.91 [-inf, 2.31167] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 97/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 40.2234
mu=0.93 [-inf, 2.24794] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 98/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 42.0372
mu=0.95 [-inf, 1.29779] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 99/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 43.891
mu=0.97 [-inf, 2.00008] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 100/100 total MC = 78 this test stat = 45.7849
mu=0.99 [-inf, 1.56062] in interval = 0
[#1] INFO:Eval -- 21 points in interval
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAbsPdf::fitTo(normal_over_normal_Int[x]) fixing normalization set for coefficient determination to observables in data
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- Creation of NLL object took 129.82 μs
[#1] INFO:Eval -- BayesianCalculator::GetPosteriorFunction : nll value 190.077 poi value = 0.99
[#1] INFO:Eval -- BayesianCalculator::GetPosteriorFunction : minimum of NLL vs POI for POI = 0.033079 min NLL = 144.292
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- Including the following constraint terms in minimization: (prior)
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- The following global observables have been defined and their values are taken from the model: ()
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAbsPdf::fitTo(product_normal_prior) fixing normalization set for coefficient determination to observables in data
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- Creation of NLL object took 1.3919 ms
[#1] INFO:Eval -- BayesianCalculator: Compute interval using RooFit: posteriorPdf + createCdf + RooBrentRootFinder
[#1] INFO:Eval -- BayesianCalculator::GetInterval - found a valid interval : [-0.95 , 0.95 ]
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- Including the following constraint terms in minimization: (prior)
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- The following global observables have been defined and their values are taken from the model: ()
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAbsPdf::fitTo(product_normal_prior) fixing normalization set for coefficient determination to observables in data
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- Creation of NLL object took 213.991 μs
Metropolis-Hastings progress: ....................................................................................................
[#1] INFO:Eval -- Proposal acceptance rate: 16.013%
[#1] INFO:Eval -- Number of steps in chain: 16013
expected interval is [-0.1629174085659928, 0.22907538834201802]
plc interval is [-0.16291740856518858, 0.22907538834189753]
fc interval is [-0.16999999999999993, 0.22999999999999998]
bc interval is [-0.95, 0.95]
mc interval is [-0.1669991221278906, 0.23022447898983955]
is mu=0 in the interval? True
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(RooEvaluatorWrapper_Profile[mu]) Creating instance of MINUIT
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAddition::defaultErrorLevel(nll_normal_over_normal_Int[x]_normalData) Summation contains a RooNLLVar, using its error level
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(RooEvaluatorWrapper_Profile[mu]) determining minimum likelihood for current configurations w.r.t all observable
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
[#0] ERROR:InputArguments -- RooArgSet::checkForDup: ERROR argument with name mu is already in this set
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(RooEvaluatorWrapper_Profile[mu]) minimum found at (mu=0.033079)
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
.[#1] INFO:Minimization -- [fitFCN] No discrete parameters, performing continuous minimization only
Real time 0:00:02, CP time 2.360