
 Standard demo of the numerical Bayesian calculator
Standard demo of the numerical Bayesian calculator
This is a standard demo that can be used with any ROOT file prepared in the standard way. You specify:
- name for input ROOT file
- name of workspace inside ROOT file that holds model and data
- name of ModelConfig that specifies details for calculator tools
- name of dataset
With default parameters the macro will attempt to run the standard hist2workspace example and read the ROOT file that it produces.
The actual heart of the demo is only about 10 lines long.
The BayesianCalculator is based on Bayes's theorem and performs the integration using ROOT's numeric integration utilities
Processing /mnt/build/workspace/root-makedoc-v612/rootspi/rdoc/src/v6-12-00-patches/tutorials/roostats/StandardBayesianNumericalDemo.C...
�[1mRooFit v3.60 -- Developed by Wouter Verkerke and David Kirkby�[0m
Copyright (C) 2000-2013 NIKHEF, University of California & Stanford University
All rights reserved, please read http://roofit.sourceforge.net/license.txt
[#1] INFO:ObjectHandling -- RooWorkspace::import(combined) importing RooUniform::prior
[#1] INFO:Minization -- p.d.f. provides expected number of events, including extended term in likelihood.
[#1] INFO:Minization -- createNLL: caching constraint set under name CONSTR_OF_PDF_simPdf_FOR_OBS_channelCat:obs_x_channel1 with 4 entries
[#1] INFO:Minization -- Including the following contraint terms in minimization: (alpha_syst2Constraint,alpha_syst3Constraint,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0_constraint,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1_constraint)
[#1] INFO:Minization -- The following global observables have been defined: (nom_alpha_syst2,nom_alpha_syst3,nom_gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0,nom_gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1)
RooAbsTestStatistic::initSimMode: creating slave calculator #0 for state channel1 (2 dataset entries)
[#1] INFO:NumericIntegration -- RooRealIntegral::init(channel1_model_Int[obs_x_channel1]) using numeric integrator RooBinIntegrator to calculate Int(obs_x_channel1)
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAbsTestStatistic::initSimMode: created 1 slave calculators.
[#1] INFO:NumericIntegration -- RooRealIntegral::init(channel1_model_Int[obs_x_channel1]) using numeric integrator RooBinIntegrator to calculate Int(obs_x_channel1)
[#1] INFO:Eval -- BayesianCalculator::GetPosteriorFunction : nll value -1033.75 poi value = 1
[#1] INFO:Eval -- BayesianCalculator::GetPosteriorFunction : minimum of NLL vs POI for POI = 1.12121 min NLL = -1033.78
[#1] INFO:InputArguments -- BayesianCalculator:GetInterval Compute the interval from the posterior cdf
[#1] INFO:NumericIntegration -- PosteriorCdfFunction - integral of posterior = 0.0560849 +/- 0.000423427
[#0] WARNING:Eval -- BayesianCalculator::GetInterval : 315 errors reported in evaluating log-likelihood function
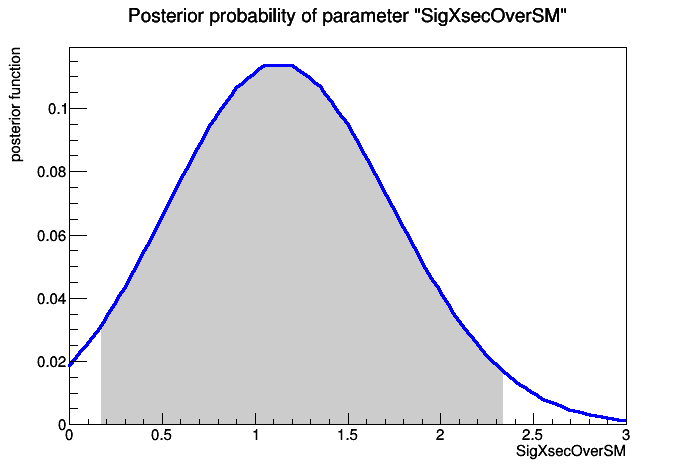
[#1] INFO:Eval -- BayesianCalculator::GetInterval - found a valid interval : [0.170773 , 2.33979 ]
>>>> RESULT : 95% interval on SigXsecOverSM is : [0.170773, 2.33979]
Drawing plot of posterior function.....
[#1] INFO:Eval -- BayesianCalculator - scan posterior function in nbins = 20
#include <cassert>
struct BayesianNumericalOptions {
double confLevel = 0.95 ;
TString integrationType = "";
int nToys = 10000;
bool scanPosterior = false;
int nScanPoints = 20;
int intervalType = 1;
double maxPOI = -999;
double nSigmaNuisance = -1;
};
BayesianNumericalOptions optBayes;
void StandardBayesianNumericalDemo(const char* infile = "",
const char* workspaceName = "combined",
const char* modelConfigName = "ModelConfig",
const char* dataName = "obsData") {
double confLevel = optBayes.confLevel;
TString integrationType = optBayes.integrationType;
int nToys = optBayes.nToys;
bool scanPosterior = optBayes.scanPosterior;
int nScanPoints = optBayes.nScanPoints;
int intervalType = optBayes.intervalType;
int maxPOI = optBayes.maxPOI;
double nSigmaNuisance = optBayes.nSigmaNuisance;
const char* filename = "";
if (!strcmp(infile,"")) {
filename = "results/example_combined_GaussExample_model.root";
if (!fileExist) {
#ifdef _WIN32
cout << "HistFactory file cannot be generated on Windows - exit" << endl;
return;
#endif
cout <<"will run standard hist2workspace example"<<endl;
gROOT->ProcessLine(
".! prepareHistFactory .");
gROOT->ProcessLine(
".! hist2workspace config/example.xml");
cout <<"\n\n---------------------"<<endl;
cout <<"Done creating example input"<<endl;
cout <<"---------------------\n\n"<<endl;
}
}
else
filename = infile;
if(!file ){
cout <<"StandardRooStatsDemoMacro: Input file " << filename << " is not found" << endl;
return;
}
if(!w){
cout <<"workspace not found" << endl;
return;
}
if(!data || !mc){
cout << "data or ModelConfig was not found" <<endl;
return;
}
if (nSigmaNuisance > 0) {
assert(pdf);
for (
int i = 0; i < nuisPar.
getSize(); ++i) {
assert( v);
std::cout <<
"setting interval for nuisance " << v->
GetName() <<
" : [ " << v->
getMin() <<
" , " << v->
getMax() <<
" ]" << std::endl;
}
}
bayesianCalc.SetConfidenceLevel(confLevel);
if (intervalType == 0) bayesianCalc.SetShortestInterval();
if (intervalType == 1) bayesianCalc.SetLeftSideTailFraction(0.5);
if (intervalType == 2) bayesianCalc.SetLeftSideTailFraction(0.);
if (!integrationType.IsNull() ) {
bayesianCalc.SetIntegrationType(integrationType);
bayesianCalc.SetNumIters(nToys);
}
if (integrationType.Contains("TOYMC") ) {
cout << "using TOYMC integration: make nuisance pdf from the model " << std::endl;
bayesianCalc.ForceNuisancePdf(*nuisPdf);
scanPosterior = true;
}
if (scanPosterior)
bayesianCalc.SetScanOfPosterior(nScanPoints);
if (maxPOI != -999 && maxPOI > poi->
getMin())
cout <<
"\n>>>> RESULT : " << confLevel*100 <<
"% interval on " << poi->
GetName()<<
" is : ["<<
cout << "\nDrawing plot of posterior function....." << endl;
bayesianCalc.SetScanOfPosterior(nScanPoints);
RooPlot * plot = bayesianCalc.GetPosteriorPlot();
}
- Author
- Kyle Cranmer
Definition in file StandardBayesianNumericalDemo.C.



 Standard demo of the numerical Bayesian calculator
Standard demo of the numerical Bayesian calculator 