// @(#)root/geom:$Name: $:$Id: TGeoShape.cxx,v 1.26 2004/11/25 12:10:01 brun Exp $
// Author: Andrei Gheata 31/01/02
/*************************************************************************
* Copyright (C) 1995-2000, Rene Brun and Fons Rademakers. *
* All rights reserved. *
* *
* For the licensing terms see $ROOTSYS/LICENSE. *
* For the list of contributors see $ROOTSYS/README/CREDITS. *
*************************************************************************/
//____________________________________________________________________________
// TGeoShape - Base abstract class for all shapes.
//____________________________________________________________________________
//
//
// Shapes are geometrical objects that provide the basic modelling
// functionality. They provide the definition of the LOCAL frame of coordinates,
// with respect to which they are defined. Any implementation of a shape deriving
// from the base TGeoShape class has to provide methods for :
// - finding out if a point defined in their local frame is or not contained
// inside;
// - computing the distance from a local point to getting outside/entering the
// shape, given a known direction;
// - computing the maximum distance in any direction from a local point that
// does NOT result in a boundary crossing of the shape (safe distance);
// - computing the cosines of the normal vector to the crossed shape surface,
// given a starting local point and an ongoing direction.
// All the features above are globally managed by the modeller in order to
// provide navigation functionality. In addition to those, shapes have also to
// implement additional specific abstract methods :
// - computation of the minimal box bounding the shape, given that this box have
// to be aligned with the local coordinates;
// - algorithms for dividing the shape along a given axis and producing resulting
// divisions volumes.
//
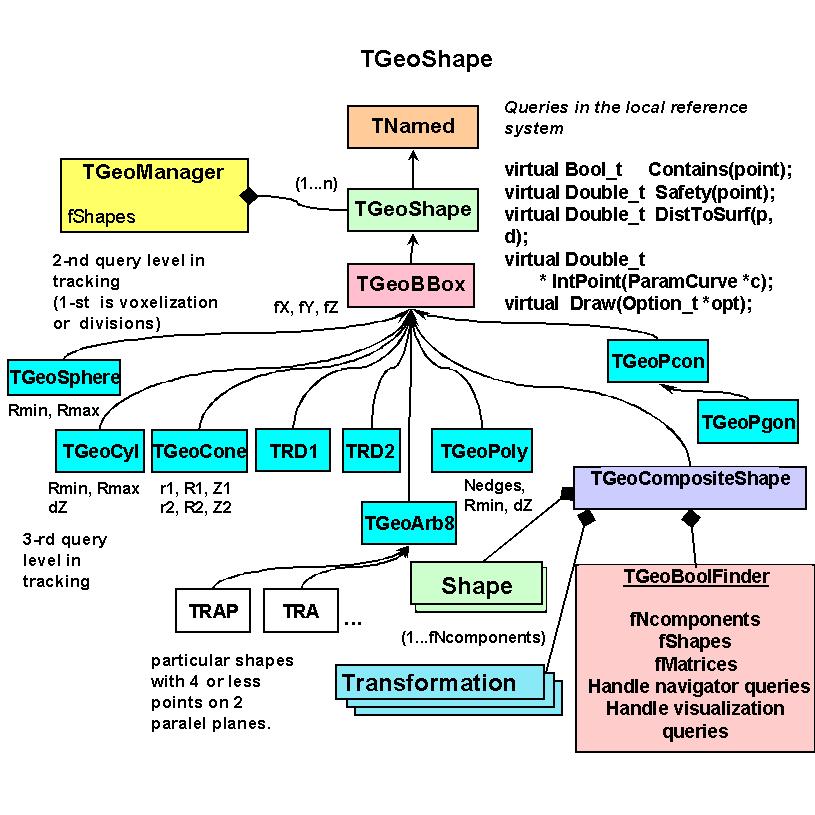
// The modeler currently provides a set of 16 basic shapes, which we will call
// primitives. It also provides a special class allowing the creation of shapes
// made as a result of boolean operations between primitives. These are called
// composite shapes and the composition operation can be recursive (composition
// of composites). This allows the creation of a quite large number of different
// shape topologies and combinations.
//
// Shapes are named objects and register themselves to the manager class at
// creation time. This is responsible for their final deletion. Shapes
// can be created without name if their retreival by name is no needed. Generally
// shapes are objects that are usefull only at geometry creation stage. The pointer
// to a shape is in fact needed only when referring to a given volume and it is
// always accessible at that level. A shape may be referenced by several volumes,
// therefore its deletion is not possible once volumes were defined based on it.
//
//
//
// Creating shapes
//================
// Shape objects embeed only the minimum set of parameters that are fully
// describing a valid physical shape. For instance, a tube is represented by
// its half length, the minimum radius and the maximum radius. Shapes are used
// togeather with media in order to create volumes, which in their turn
// are the main components of the geometrical tree. A specific shape can be created
// stand-alone :
//
// TGeoBBox *box = new TGeoBBox("s_box", halfX, halfY, halfZ); // named
// TGeoTube *tub = new TGeoTube(rmin, rmax, halfZ); // no name
// ... (see each specific shape constructors)
//
// Sometimes it is much easier to create a volume having a given shape in one
// step, since shapes are not direcly linked in the geometrical tree but volumes
// are :
//
// TGeoVolume *vol_box = gGeoManager->MakeBox("BOX_VOL", "mat1", halfX, halfY, halfZ);
// TGeoVolume *vol_tub = gGeoManager->MakeTube("TUB_VOL", "mat2", rmin, rmax, halfZ);
// ... (see MakeXXX() utilities in TGeoManager class)
//
//
// Shape queries
//===============
// Note that global queries related to a geometry are handled by the manager class.
// However, shape-related queries might be sometimes usefull.
//
// A) Bool_t TGeoShape::Contains(Double_t *point[3])
// - this method returns true if POINT is actually inside the shape. The point
// has to be defined in the local shape reference. For instance, for a box having
// DX, DY and DZ half-lengths a point will be considered inside if :
// | -DX <= point[0] <= DX
// | -DY <= point[1] <= DY
// | -DZ <= point[2] <= DZ
//
// B) Double_t TGeoShape::DistFromInside(Double_t *point[3], Double_t *dir[3],
// Int_t iact, Double_t step, Double_t *safe)
// - computes the distance to exiting a shape from a given point INSIDE, along
// a given direction. The direction is given by its director cosines with respect
// to the local shape coordinate system. This method provides additional
// information according the value of IACT input parameter :
// IACT = 0 => compute only safe distance and fill it at the location
// given by SAFE
// IACT = 1 => a proposed STEP is supplied. The safe distance is computed
// first. If this is bigger than STEP than the proposed step
// is approved and returned by the method since it does not
// cross the shape boundaries. Otherwise, the distance to
// exiting the shape is computed and returned.
// IACT = 2 => compute both safe distance and distance to exiting, ignoring
// the proposed step.
// IACT > 2 => compute only the distance to exiting, ignoring anything else.
//
// C) Double_t TGeoShape::DistFromOutside(Double_t *point[3], Double_t *dir[3],
// Int_t iact, Double_t step, Double_t *safe)
// - computes the distance to entering a shape from a given point OUTSIDE. Acts
// in the same way as B).
//
// D) Double_t Safety(Double_t *point[3], Bool_t inside)
//
// - compute maximum shift of a point in any direction that does not change its
// INSIDE/OUTSIDE state (does not cross shape boundaries). The state of the point
// have to be properly supplied.
//
// E) Double_t *Normal(Double_t *point[3], Double_t *dir[3], Bool_t inside)
//
// - returns director cosines of normal to the crossed shape surface from a
// given point towards a direction. One has to specify if the point is inside
// or outside shape. According to this, the normal will be outwards or inwards
// shape respectively. Normal components are statically stored by shape class,
// so it has to be copied after retreival in a different array.
//
// Dividing shapes
//=================
// Shapes can generally be divided along a given axis. Supported axis are
// X, Y, Z, Rxy, Phi, Rxyz. A given shape cannot be divided however on any axis.
// The general rule is that that divisions are possible on whatever axis that
// produces still known shapes as slices. The division of shapes should not be
// performed by TGeoShape::Divide() calls, but rather by TGeoVolume::Divide().
// The algorithm for dividing a specific shape is known by the shape object, but
// is always invoked in a generic way from the volume level. Details on how to
// do that can be found in TGeoVolume class. One can see how all division options
// are interpreted and which is their result inside specific shape classes.
//_____________________________________________________________________________
//
//
/*
 */
//
#include "TObjArray.h"
#include "TGeoMatrix.h"
#include "TGeoManager.h"
#include "TGeoVolume.h"
#include "TGeoShape.h"
#include "TVirtualGeoPainter.h"
ClassImp(TGeoShape)
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::TGeoShape()
{
// Default constructor
fShapeBits = 0;
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
// fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
// gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::TGeoShape(const char *name)
:TNamed(name, "")
{
// Default constructor
fShapeBits = 0;
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::~TGeoShape()
{
// Destructor
if (gGeoManager) gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->Remove(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
const char *TGeoShape::GetName() const
{
if (!strlen(fName)) {
return ((TObject *)this)->ClassName();
}
return TNamed::GetName();
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TGeoShape::ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(Int_t numpoints, Int_t px, Int_t py) const
{
TVirtualGeoPainter *painter = gGeoManager->GetGeomPainter();
if (!painter) return 9999;
return painter->ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(this, numpoints, px, py);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsCloseToPhi(Double_t epsil, Double_t *point, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// True if point is closer than epsil to one of the phi planes defined by c1,s1 or c2,s2
Double_t saf1 = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t saf2 = TGeoShape::Big();
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = TMath::Abs(-point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1);
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = TMath::Abs(point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2);
Double_t saf = TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
if (saf<epsil) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsInPhiRange(Double_t *point, Double_t phi1, Double_t phi2)
{
// Static method to check if a point is in the phi range (phi1, phi2) [degrees]
Double_t phi = TMath::ATan2(point[1], point[0]) * TMath::RadToDeg();
while (phi<phi1) phi+=360.;
Double_t ddp = phi-phi1;
if (ddp>phi2-phi1) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsCrossingSemiplane(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Double_t cphi, Double_t sphi, Double_t &snext, Double_t &rxy)
{
// Compute distance from POINT to semiplane defined by PHI angle along DIR. Computes
// also radius at crossing point. This might be negative in case the crossing is
// on the other side of the semiplane.
snext = rxy = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t ndot = dir[1]*cphi-dir[0]*sphi;
if (TMath::Abs(ndot)<1E-10) return kFALSE;
Double_t ndinv = 1./ndot;
snext = (point[0]*sphi-point[1]*cphi)*ndinv;
if (snext<0) return kFALSE;
rxy = (point[0]*dir[1]-point[1]*dir[0])*ndinv;
if (rxy<0) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::NormalPhi(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Double_t *norm, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// Static method to compute normal to phi planes.
Double_t saf1 = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t saf2 = TGeoShape::Big();
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = TMath::Abs(-point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1);
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = TMath::Abs(point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2);
Double_t c,s;
if (saf1<saf2) {
c=c1;
s=s1;
} else {
c=c2;
s=s2;
}
norm[2] = 0;
norm[0] = -s;
norm[1] = c;
if (dir[0]*norm[0]+dir[1]*norm[1] < 0) {
norm[0] = s;
norm[1] = -c;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TGeoShape::SafetyPhi(Double_t *point, Bool_t in, Double_t phi1, Double_t phi2)
{
// Static method to compute safety w.r.t a phi corner defined by cosines/sines
// of the angles phi1, phi2.
Bool_t inphi = TGeoShape::IsInPhiRange(point, phi1, phi2);
if (inphi && !in) return -TGeoShape::Big();
phi1 *= TMath::DegToRad();
phi2 *= TMath::DegToRad();
Double_t c1 = TMath::Cos(phi1);
Double_t s1 = TMath::Sin(phi1);
Double_t c2 = TMath::Cos(phi2);
Double_t s2 = TMath::Sin(phi2);
Double_t rsq = point[0]*point[0]+point[1]*point[1];
Double_t rproj = point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1;
Double_t safsq = rsq-rproj*rproj;
if (safsq<0) return 0.;
Double_t saf1 = (rproj<0)?TGeoShape::Big():TMath::Sqrt(safsq);
rproj = point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2;
safsq = rsq-rproj*rproj;
if (safsq<0) return 0.;
Double_t saf2 = (rproj<0)?TGeoShape::Big():TMath::Sqrt(safsq);
Double_t safe = TMath::Min(saf1, saf2); // >0
if (safe>1E10) {
if (in) return TGeoShape::Big();
return -TGeoShape::Big();
}
return safe;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::SetShapeBit(UInt_t f, Bool_t set)
{
if (set) {
SetShapeBit(f);
} else {
ResetShapeBit(f);
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::TransformPoints(TBuffer3D *buff) const
{
// Tranform a buffer (LocalToMaster)
// Set reflection flag and transparency
if (gGeoManager) {
Bool_t isReflection = gGeoManager->IsMatrixReflection();
buff->SetBit(TBuffer3D::kIsReflection, isReflection);
TGeoVolume *vol = gGeoManager->GetPaintVolume();
buff->fTransparency = (vol==0)?0:vol->GetTransparency();
Double_t visdensity = gGeoManager->GetVisDensity();
if (visdensity>0 && vol->GetMedium()) {
if (vol->GetMaterial()->GetDensity() < visdensity) buff->fTransparency = 90;
}
Double_t dlocal[3];
Double_t dmaster[3];
Bool_t bomb = (gGeoManager->GetBombMode()==0)?kFALSE:kTRUE;
for (Int_t j = 0; j < buff->fNbPnts; j++) {
dlocal[0] = buff->fPnts[3*j];
dlocal[1] = buff->fPnts[3*j+1];
dlocal[2] = buff->fPnts[3*j+2];
if (gGeoManager->IsMatrixTransform()) {
TGeoHMatrix *glmat = gGeoManager->GetGLMatrix();
if (bomb) glmat->LocalToMasterBomb(dlocal, dmaster);
else glmat->LocalToMaster(dlocal, dmaster);
} else {
if (bomb) gGeoManager->LocalToMasterBomb(dlocal, dmaster);
else gGeoManager->LocalToMaster(dlocal,dmaster);
}
buff->fPnts[3*j] = dmaster[0];
buff->fPnts[3*j+1] = dmaster[1];
buff->fPnts[3*j+2] = dmaster[2];
}
}
}
*/
//
#include "TObjArray.h"
#include "TGeoMatrix.h"
#include "TGeoManager.h"
#include "TGeoVolume.h"
#include "TGeoShape.h"
#include "TVirtualGeoPainter.h"
ClassImp(TGeoShape)
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::TGeoShape()
{
// Default constructor
fShapeBits = 0;
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
// fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
// gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::TGeoShape(const char *name)
:TNamed(name, "")
{
// Default constructor
fShapeBits = 0;
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::~TGeoShape()
{
// Destructor
if (gGeoManager) gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->Remove(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
const char *TGeoShape::GetName() const
{
if (!strlen(fName)) {
return ((TObject *)this)->ClassName();
}
return TNamed::GetName();
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TGeoShape::ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(Int_t numpoints, Int_t px, Int_t py) const
{
TVirtualGeoPainter *painter = gGeoManager->GetGeomPainter();
if (!painter) return 9999;
return painter->ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(this, numpoints, px, py);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsCloseToPhi(Double_t epsil, Double_t *point, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// True if point is closer than epsil to one of the phi planes defined by c1,s1 or c2,s2
Double_t saf1 = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t saf2 = TGeoShape::Big();
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = TMath::Abs(-point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1);
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = TMath::Abs(point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2);
Double_t saf = TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
if (saf<epsil) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsInPhiRange(Double_t *point, Double_t phi1, Double_t phi2)
{
// Static method to check if a point is in the phi range (phi1, phi2) [degrees]
Double_t phi = TMath::ATan2(point[1], point[0]) * TMath::RadToDeg();
while (phi<phi1) phi+=360.;
Double_t ddp = phi-phi1;
if (ddp>phi2-phi1) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsCrossingSemiplane(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Double_t cphi, Double_t sphi, Double_t &snext, Double_t &rxy)
{
// Compute distance from POINT to semiplane defined by PHI angle along DIR. Computes
// also radius at crossing point. This might be negative in case the crossing is
// on the other side of the semiplane.
snext = rxy = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t ndot = dir[1]*cphi-dir[0]*sphi;
if (TMath::Abs(ndot)<1E-10) return kFALSE;
Double_t ndinv = 1./ndot;
snext = (point[0]*sphi-point[1]*cphi)*ndinv;
if (snext<0) return kFALSE;
rxy = (point[0]*dir[1]-point[1]*dir[0])*ndinv;
if (rxy<0) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::NormalPhi(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Double_t *norm, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// Static method to compute normal to phi planes.
Double_t saf1 = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t saf2 = TGeoShape::Big();
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = TMath::Abs(-point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1);
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = TMath::Abs(point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2);
Double_t c,s;
if (saf1<saf2) {
c=c1;
s=s1;
} else {
c=c2;
s=s2;
}
norm[2] = 0;
norm[0] = -s;
norm[1] = c;
if (dir[0]*norm[0]+dir[1]*norm[1] < 0) {
norm[0] = s;
norm[1] = -c;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TGeoShape::SafetyPhi(Double_t *point, Bool_t in, Double_t phi1, Double_t phi2)
{
// Static method to compute safety w.r.t a phi corner defined by cosines/sines
// of the angles phi1, phi2.
Bool_t inphi = TGeoShape::IsInPhiRange(point, phi1, phi2);
if (inphi && !in) return -TGeoShape::Big();
phi1 *= TMath::DegToRad();
phi2 *= TMath::DegToRad();
Double_t c1 = TMath::Cos(phi1);
Double_t s1 = TMath::Sin(phi1);
Double_t c2 = TMath::Cos(phi2);
Double_t s2 = TMath::Sin(phi2);
Double_t rsq = point[0]*point[0]+point[1]*point[1];
Double_t rproj = point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1;
Double_t safsq = rsq-rproj*rproj;
if (safsq<0) return 0.;
Double_t saf1 = (rproj<0)?TGeoShape::Big():TMath::Sqrt(safsq);
rproj = point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2;
safsq = rsq-rproj*rproj;
if (safsq<0) return 0.;
Double_t saf2 = (rproj<0)?TGeoShape::Big():TMath::Sqrt(safsq);
Double_t safe = TMath::Min(saf1, saf2); // >0
if (safe>1E10) {
if (in) return TGeoShape::Big();
return -TGeoShape::Big();
}
return safe;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::SetShapeBit(UInt_t f, Bool_t set)
{
if (set) {
SetShapeBit(f);
} else {
ResetShapeBit(f);
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::TransformPoints(TBuffer3D *buff) const
{
// Tranform a buffer (LocalToMaster)
// Set reflection flag and transparency
if (gGeoManager) {
Bool_t isReflection = gGeoManager->IsMatrixReflection();
buff->SetBit(TBuffer3D::kIsReflection, isReflection);
TGeoVolume *vol = gGeoManager->GetPaintVolume();
buff->fTransparency = (vol==0)?0:vol->GetTransparency();
Double_t visdensity = gGeoManager->GetVisDensity();
if (visdensity>0 && vol->GetMedium()) {
if (vol->GetMaterial()->GetDensity() < visdensity) buff->fTransparency = 90;
}
Double_t dlocal[3];
Double_t dmaster[3];
Bool_t bomb = (gGeoManager->GetBombMode()==0)?kFALSE:kTRUE;
for (Int_t j = 0; j < buff->fNbPnts; j++) {
dlocal[0] = buff->fPnts[3*j];
dlocal[1] = buff->fPnts[3*j+1];
dlocal[2] = buff->fPnts[3*j+2];
if (gGeoManager->IsMatrixTransform()) {
TGeoHMatrix *glmat = gGeoManager->GetGLMatrix();
if (bomb) glmat->LocalToMasterBomb(dlocal, dmaster);
else glmat->LocalToMaster(dlocal, dmaster);
} else {
if (bomb) gGeoManager->LocalToMasterBomb(dlocal, dmaster);
else gGeoManager->LocalToMaster(dlocal,dmaster);
}
buff->fPnts[3*j] = dmaster[0];
buff->fPnts[3*j+1] = dmaster[1];
buff->fPnts[3*j+2] = dmaster[2];
}
}
}
ROOT page - Class index - Class Hierarchy - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
 */
//
#include "TObjArray.h"
#include "TGeoMatrix.h"
#include "TGeoManager.h"
#include "TGeoVolume.h"
#include "TGeoShape.h"
#include "TVirtualGeoPainter.h"
ClassImp(TGeoShape)
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::TGeoShape()
{
// Default constructor
fShapeBits = 0;
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
// fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
// gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::TGeoShape(const char *name)
:TNamed(name, "")
{
// Default constructor
fShapeBits = 0;
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::~TGeoShape()
{
// Destructor
if (gGeoManager) gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->Remove(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
const char *TGeoShape::GetName() const
{
if (!strlen(fName)) {
return ((TObject *)this)->ClassName();
}
return TNamed::GetName();
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TGeoShape::ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(Int_t numpoints, Int_t px, Int_t py) const
{
TVirtualGeoPainter *painter = gGeoManager->GetGeomPainter();
if (!painter) return 9999;
return painter->ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(this, numpoints, px, py);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsCloseToPhi(Double_t epsil, Double_t *point, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// True if point is closer than epsil to one of the phi planes defined by c1,s1 or c2,s2
Double_t saf1 = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t saf2 = TGeoShape::Big();
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = TMath::Abs(-point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1);
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = TMath::Abs(point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2);
Double_t saf = TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
if (saf<epsil) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsInPhiRange(Double_t *point, Double_t phi1, Double_t phi2)
{
// Static method to check if a point is in the phi range (phi1, phi2) [degrees]
Double_t phi = TMath::ATan2(point[1], point[0]) * TMath::RadToDeg();
while (phi<phi1) phi+=360.;
Double_t ddp = phi-phi1;
if (ddp>phi2-phi1) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsCrossingSemiplane(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Double_t cphi, Double_t sphi, Double_t &snext, Double_t &rxy)
{
// Compute distance from POINT to semiplane defined by PHI angle along DIR. Computes
// also radius at crossing point. This might be negative in case the crossing is
// on the other side of the semiplane.
snext = rxy = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t ndot = dir[1]*cphi-dir[0]*sphi;
if (TMath::Abs(ndot)<1E-10) return kFALSE;
Double_t ndinv = 1./ndot;
snext = (point[0]*sphi-point[1]*cphi)*ndinv;
if (snext<0) return kFALSE;
rxy = (point[0]*dir[1]-point[1]*dir[0])*ndinv;
if (rxy<0) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::NormalPhi(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Double_t *norm, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// Static method to compute normal to phi planes.
Double_t saf1 = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t saf2 = TGeoShape::Big();
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = TMath::Abs(-point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1);
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = TMath::Abs(point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2);
Double_t c,s;
if (saf1<saf2) {
c=c1;
s=s1;
} else {
c=c2;
s=s2;
}
norm[2] = 0;
norm[0] = -s;
norm[1] = c;
if (dir[0]*norm[0]+dir[1]*norm[1] < 0) {
norm[0] = s;
norm[1] = -c;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TGeoShape::SafetyPhi(Double_t *point, Bool_t in, Double_t phi1, Double_t phi2)
{
// Static method to compute safety w.r.t a phi corner defined by cosines/sines
// of the angles phi1, phi2.
Bool_t inphi = TGeoShape::IsInPhiRange(point, phi1, phi2);
if (inphi && !in) return -TGeoShape::Big();
phi1 *= TMath::DegToRad();
phi2 *= TMath::DegToRad();
Double_t c1 = TMath::Cos(phi1);
Double_t s1 = TMath::Sin(phi1);
Double_t c2 = TMath::Cos(phi2);
Double_t s2 = TMath::Sin(phi2);
Double_t rsq = point[0]*point[0]+point[1]*point[1];
Double_t rproj = point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1;
Double_t safsq = rsq-rproj*rproj;
if (safsq<0) return 0.;
Double_t saf1 = (rproj<0)?TGeoShape::Big():TMath::Sqrt(safsq);
rproj = point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2;
safsq = rsq-rproj*rproj;
if (safsq<0) return 0.;
Double_t saf2 = (rproj<0)?TGeoShape::Big():TMath::Sqrt(safsq);
Double_t safe = TMath::Min(saf1, saf2); // >0
if (safe>1E10) {
if (in) return TGeoShape::Big();
return -TGeoShape::Big();
}
return safe;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::SetShapeBit(UInt_t f, Bool_t set)
{
if (set) {
SetShapeBit(f);
} else {
ResetShapeBit(f);
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::TransformPoints(TBuffer3D *buff) const
{
// Tranform a buffer (LocalToMaster)
// Set reflection flag and transparency
if (gGeoManager) {
Bool_t isReflection = gGeoManager->IsMatrixReflection();
buff->SetBit(TBuffer3D::kIsReflection, isReflection);
TGeoVolume *vol = gGeoManager->GetPaintVolume();
buff->fTransparency = (vol==0)?0:vol->GetTransparency();
Double_t visdensity = gGeoManager->GetVisDensity();
if (visdensity>0 && vol->GetMedium()) {
if (vol->GetMaterial()->GetDensity() < visdensity) buff->fTransparency = 90;
}
Double_t dlocal[3];
Double_t dmaster[3];
Bool_t bomb = (gGeoManager->GetBombMode()==0)?kFALSE:kTRUE;
for (Int_t j = 0; j < buff->fNbPnts; j++) {
dlocal[0] = buff->fPnts[3*j];
dlocal[1] = buff->fPnts[3*j+1];
dlocal[2] = buff->fPnts[3*j+2];
if (gGeoManager->IsMatrixTransform()) {
TGeoHMatrix *glmat = gGeoManager->GetGLMatrix();
if (bomb) glmat->LocalToMasterBomb(dlocal, dmaster);
else glmat->LocalToMaster(dlocal, dmaster);
} else {
if (bomb) gGeoManager->LocalToMasterBomb(dlocal, dmaster);
else gGeoManager->LocalToMaster(dlocal,dmaster);
}
buff->fPnts[3*j] = dmaster[0];
buff->fPnts[3*j+1] = dmaster[1];
buff->fPnts[3*j+2] = dmaster[2];
}
}
}
*/
//
#include "TObjArray.h"
#include "TGeoMatrix.h"
#include "TGeoManager.h"
#include "TGeoVolume.h"
#include "TGeoShape.h"
#include "TVirtualGeoPainter.h"
ClassImp(TGeoShape)
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::TGeoShape()
{
// Default constructor
fShapeBits = 0;
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
// fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
// gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::TGeoShape(const char *name)
:TNamed(name, "")
{
// Default constructor
fShapeBits = 0;
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
TGeoShape::~TGeoShape()
{
// Destructor
if (gGeoManager) gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->Remove(this);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
const char *TGeoShape::GetName() const
{
if (!strlen(fName)) {
return ((TObject *)this)->ClassName();
}
return TNamed::GetName();
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TGeoShape::ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(Int_t numpoints, Int_t px, Int_t py) const
{
TVirtualGeoPainter *painter = gGeoManager->GetGeomPainter();
if (!painter) return 9999;
return painter->ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(this, numpoints, px, py);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsCloseToPhi(Double_t epsil, Double_t *point, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// True if point is closer than epsil to one of the phi planes defined by c1,s1 or c2,s2
Double_t saf1 = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t saf2 = TGeoShape::Big();
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = TMath::Abs(-point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1);
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = TMath::Abs(point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2);
Double_t saf = TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
if (saf<epsil) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsInPhiRange(Double_t *point, Double_t phi1, Double_t phi2)
{
// Static method to check if a point is in the phi range (phi1, phi2) [degrees]
Double_t phi = TMath::ATan2(point[1], point[0]) * TMath::RadToDeg();
while (phi<phi1) phi+=360.;
Double_t ddp = phi-phi1;
if (ddp>phi2-phi1) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TGeoShape::IsCrossingSemiplane(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Double_t cphi, Double_t sphi, Double_t &snext, Double_t &rxy)
{
// Compute distance from POINT to semiplane defined by PHI angle along DIR. Computes
// also radius at crossing point. This might be negative in case the crossing is
// on the other side of the semiplane.
snext = rxy = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t ndot = dir[1]*cphi-dir[0]*sphi;
if (TMath::Abs(ndot)<1E-10) return kFALSE;
Double_t ndinv = 1./ndot;
snext = (point[0]*sphi-point[1]*cphi)*ndinv;
if (snext<0) return kFALSE;
rxy = (point[0]*dir[1]-point[1]*dir[0])*ndinv;
if (rxy<0) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::NormalPhi(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Double_t *norm, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// Static method to compute normal to phi planes.
Double_t saf1 = TGeoShape::Big();
Double_t saf2 = TGeoShape::Big();
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = TMath::Abs(-point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1);
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = TMath::Abs(point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2);
Double_t c,s;
if (saf1<saf2) {
c=c1;
s=s1;
} else {
c=c2;
s=s2;
}
norm[2] = 0;
norm[0] = -s;
norm[1] = c;
if (dir[0]*norm[0]+dir[1]*norm[1] < 0) {
norm[0] = s;
norm[1] = -c;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TGeoShape::SafetyPhi(Double_t *point, Bool_t in, Double_t phi1, Double_t phi2)
{
// Static method to compute safety w.r.t a phi corner defined by cosines/sines
// of the angles phi1, phi2.
Bool_t inphi = TGeoShape::IsInPhiRange(point, phi1, phi2);
if (inphi && !in) return -TGeoShape::Big();
phi1 *= TMath::DegToRad();
phi2 *= TMath::DegToRad();
Double_t c1 = TMath::Cos(phi1);
Double_t s1 = TMath::Sin(phi1);
Double_t c2 = TMath::Cos(phi2);
Double_t s2 = TMath::Sin(phi2);
Double_t rsq = point[0]*point[0]+point[1]*point[1];
Double_t rproj = point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1;
Double_t safsq = rsq-rproj*rproj;
if (safsq<0) return 0.;
Double_t saf1 = (rproj<0)?TGeoShape::Big():TMath::Sqrt(safsq);
rproj = point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2;
safsq = rsq-rproj*rproj;
if (safsq<0) return 0.;
Double_t saf2 = (rproj<0)?TGeoShape::Big():TMath::Sqrt(safsq);
Double_t safe = TMath::Min(saf1, saf2); // >0
if (safe>1E10) {
if (in) return TGeoShape::Big();
return -TGeoShape::Big();
}
return safe;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::SetShapeBit(UInt_t f, Bool_t set)
{
if (set) {
SetShapeBit(f);
} else {
ResetShapeBit(f);
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TGeoShape::TransformPoints(TBuffer3D *buff) const
{
// Tranform a buffer (LocalToMaster)
// Set reflection flag and transparency
if (gGeoManager) {
Bool_t isReflection = gGeoManager->IsMatrixReflection();
buff->SetBit(TBuffer3D::kIsReflection, isReflection);
TGeoVolume *vol = gGeoManager->GetPaintVolume();
buff->fTransparency = (vol==0)?0:vol->GetTransparency();
Double_t visdensity = gGeoManager->GetVisDensity();
if (visdensity>0 && vol->GetMedium()) {
if (vol->GetMaterial()->GetDensity() < visdensity) buff->fTransparency = 90;
}
Double_t dlocal[3];
Double_t dmaster[3];
Bool_t bomb = (gGeoManager->GetBombMode()==0)?kFALSE:kTRUE;
for (Int_t j = 0; j < buff->fNbPnts; j++) {
dlocal[0] = buff->fPnts[3*j];
dlocal[1] = buff->fPnts[3*j+1];
dlocal[2] = buff->fPnts[3*j+2];
if (gGeoManager->IsMatrixTransform()) {
TGeoHMatrix *glmat = gGeoManager->GetGLMatrix();
if (bomb) glmat->LocalToMasterBomb(dlocal, dmaster);
else glmat->LocalToMaster(dlocal, dmaster);
} else {
if (bomb) gGeoManager->LocalToMasterBomb(dlocal, dmaster);
else gGeoManager->LocalToMaster(dlocal,dmaster);
}
buff->fPnts[3*j] = dmaster[0];
buff->fPnts[3*j+1] = dmaster[1];
buff->fPnts[3*j+2] = dmaster[2];
}
}
}