| library: libTMVA #include "MethodLikelihood.h" |
| virtual void | DeclareOptions() |
| void | InitLik() |
| virtual void | ProcessOptions() |
| enum TMVA::MethodBase::EWeightFileType { | kROOT | |
| kTEXT | ||
| }; | ||
| enum TMVA::MethodBase::ECutOrientation { | kNegative | |
| kPositive | ||
| }; | ||
| enum TObject::EStatusBits { | kCanDelete | |
| kMustCleanup | ||
| kObjInCanvas | ||
| kIsReferenced | ||
| kHasUUID | ||
| kCannotPick | ||
| kNoContextMenu | ||
| kInvalidObject | ||
| }; | ||
| enum TObject::[unnamed] { | kIsOnHeap | |
| kNotDeleted | ||
| kZombie | ||
| kBitMask | ||
| kSingleKey | ||
| kOverwrite | ||
| kWriteDelete | ||
| }; |
| TMVA::Ranking* | TMVA::MethodBase::fRanking | ranking |
| vector<TString>* | TMVA::MethodBase::fInputVars | vector of input variables used in MVA |
| Bool_t | TMVA::MethodBase::fIsOK | status of sanity checks |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fHistS_plotbin | MVA plots used for graphics representation (signal) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fHistB_plotbin | MVA plots used for graphics representation (background) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fHistS_highbin | MVA plots used for efficiency calculations (signal) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fHistB_highbin | MVA plots used for efficiency calculations (background) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fEffS | efficiency plot (signal) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fEffB | efficiency plot (background) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fEffBvsS | background efficiency versus signal efficiency |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fRejBvsS | background rejection (=1-eff.) versus signal efficiency |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fHistBhatS | working histograms needed for mu-transform (signal) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fHistBhatB | working histograms needed for mu-transform (background) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fHistMuS | mu-transform (signal) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fHistMuB | mu-transform (background) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fTrainEffS | Training efficiency plot (signal) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fTrainEffB | Training efficiency plot (background) |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fTrainEffBvsS | Training background efficiency versus signal efficiency |
| TH1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fTrainRejBvsS | Training background rejection (=1-eff.) versus signal efficiency |
| Double_t | TMVA::MethodBase::fX | |
| Double_t | TMVA::MethodBase::fMode | |
| TGraph* | TMVA::MethodBase::fGraphS | graphs used for splines for efficiency (signal) |
| TGraph* | TMVA::MethodBase::fGraphB | graphs used for splines for efficiency (background) |
| TGraph* | TMVA::MethodBase::fGrapheffBvsS | graphs used for splines for signal eff. versus background eff. |
| TMVA::PDF* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSplS | PDFs of MVA distribution (signal) |
| TMVA::PDF* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSplB | PDFs of MVA distribution (background) |
| TSpline* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSpleffBvsS | splines for signal eff. versus background eff. |
| TGraph* | TMVA::MethodBase::fGraphTrainS | graphs used for splines for training efficiency (signal) |
| TGraph* | TMVA::MethodBase::fGraphTrainB | graphs used for splines for training efficiency (background) |
| TGraph* | TMVA::MethodBase::fGraphTrainEffBvsS | graphs used for splines for training signal eff. versus background eff. |
| TMVA::PDF* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSplTrainS | PDFs of training MVA distribution (signal) |
| TMVA::PDF* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSplTrainB | PDFs of training MVA distribution (background) |
| TSpline* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSplTrainEffBvsS | splines for training signal eff. versus background eff. |
| Int_t | TMVA::MethodBase::fNbins | number of bins in representative histograms |
| Int_t | TMVA::MethodBase::fNbinsH | number of bins in evaluation histograms |
| TMVA::MethodBase::ECutOrientation | TMVA::MethodBase::fCutOrientation | +1 if Sig>Bkg, -1 otherwise |
| TMVA::TSpline1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSplRefS | helper splines for RootFinder (signal) |
| TMVA::TSpline1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSplRefB | helper splines for RootFinder (background) |
| TMVA::TSpline1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSplTrainRefS | helper splines for RootFinder (signal) |
| TMVA::TSpline1* | TMVA::MethodBase::fSplTrainRefB | helper splines for RootFinder (background) |
| TMVA::OptionBase* | TMVA::MethodBase::fLastDeclaredOption | last declared option |
| TList | TMVA::MethodBase::fListOfOptions | option list |
| TMVA::MsgLogger | TMVA::MethodBase::fLogger | message logger |
| Int_t | fSpline | Spline order to smooth histograms |
| Int_t | fAverageEvtPerBin | average events per bin; used to calculate fNbins |
| TMVA::PDF::ESmoothMethod | fSmoothMethod | |
| TFile* | fFin | |
| Int_t | fNsmooth | naumber of smooth passes |
| Double_t | fEpsilon | minimum number of likelihood (to avoid zero) |
| Bool_t | fTransformLikelihoodOutput | likelihood output is sigmoid-transformed |
| vector<TH1*>* | fHistSig | signal PDFs (histograms) |
| vector<TH1*>* | fHistBgd | background PDFs (histograms) |
| vector<TH1*>* | fHistSig_smooth | signal PDFs (smoothed histograms) |
| vector<TH1*>* | fHistBgd_smooth | background PDFs (smoothed histograms) |
| TList* | fSigPDFHist | list of PDF histograms (signal) |
| TList* | fBgdPDFHist | list of PDF histograms (background) |
| vector<UInt_t>* | fIndexSig | used for caching in GetMvaValue |
| vector<UInt_t>* | fIndexBgd | used for caching in GetMvaValue |
| vector<PDF*>* | fPDFSig | list of PDFs (signal) |
| vector<PDF*>* | fPDFBgd | list of PDFs (background) |
/* Likelihood analysis ("non-parametric approach")
Also implemented is a "diagonalized likelihood approach", which improves over the uncorrelated likelihood ansatz by transforming linearly the input variables into a diagonal space, using the square-root of the covariance matrix
The method of maximum likelihood is the most straightforward, and
certainly among the most elegant multivariate analyser approaches.
We define the likelihood ratio, RL, for event
i, by:

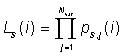
Note that in TMVA the output of the likelihood ratio is transformed
by

The biggest drawback of the Likelihood approach is that it assumes
that the discriminant variables are uncorrelated. If it were the case,
it can be proven that the discrimination obtained by the above likelihood
ratio is optimal, ie, no other method can beat it. However, in most
practical applications of MVAs correlations are present.
Linear correlations, measured from the training sample, can be taken
into account in a straightforward manner through the square-root
of the covariance matrix. The square-root of a matrix
C is the matrix C′ that multiplied with itself
yields C: C=C′C′. We compute the
square-root matrix (SQM) by means of diagonalising (D) the
covariance matrix:

The above diagonalisation is complete for linearly correlated, Gaussian distributed variables only. In real-world examples this is not often the case, so that only little additional information may be recovered by the diagonalisation procedure. In these cases, non-linear methods must be applied. */
_______________________________________________________________________
standard constructor MethodLikelihood options: format and syntax of option string: "Spline2:0:25:D" where: SplineI [I=0,12,3,5] - which spline is used for smoothing the pdfs 0 - how often the input histos are smoothed 25 - average num of events per PDF bin to trigger warning D - use square-root-matrix to decorrelate variable space
construct likelihood references from file
define the options (their key words) that can be set in the option string know options: Spline <int> spline used to interpolate reference histograms available values are: 0, 1, 2 <default>, 3, 5 NSmooth <int> how often the input histos are smoothed NAvEvtPerBin <int> minimum average number of events per PDF bin (less trigger warning) TransformOutput <bool> transform (often strongly peaked) likelihood output through sigmoid inversion
create reference distributions (PDFs) from signal and background events: fill histograms and smooth them; if decorrelation is required, compute corresponding square-root matrices