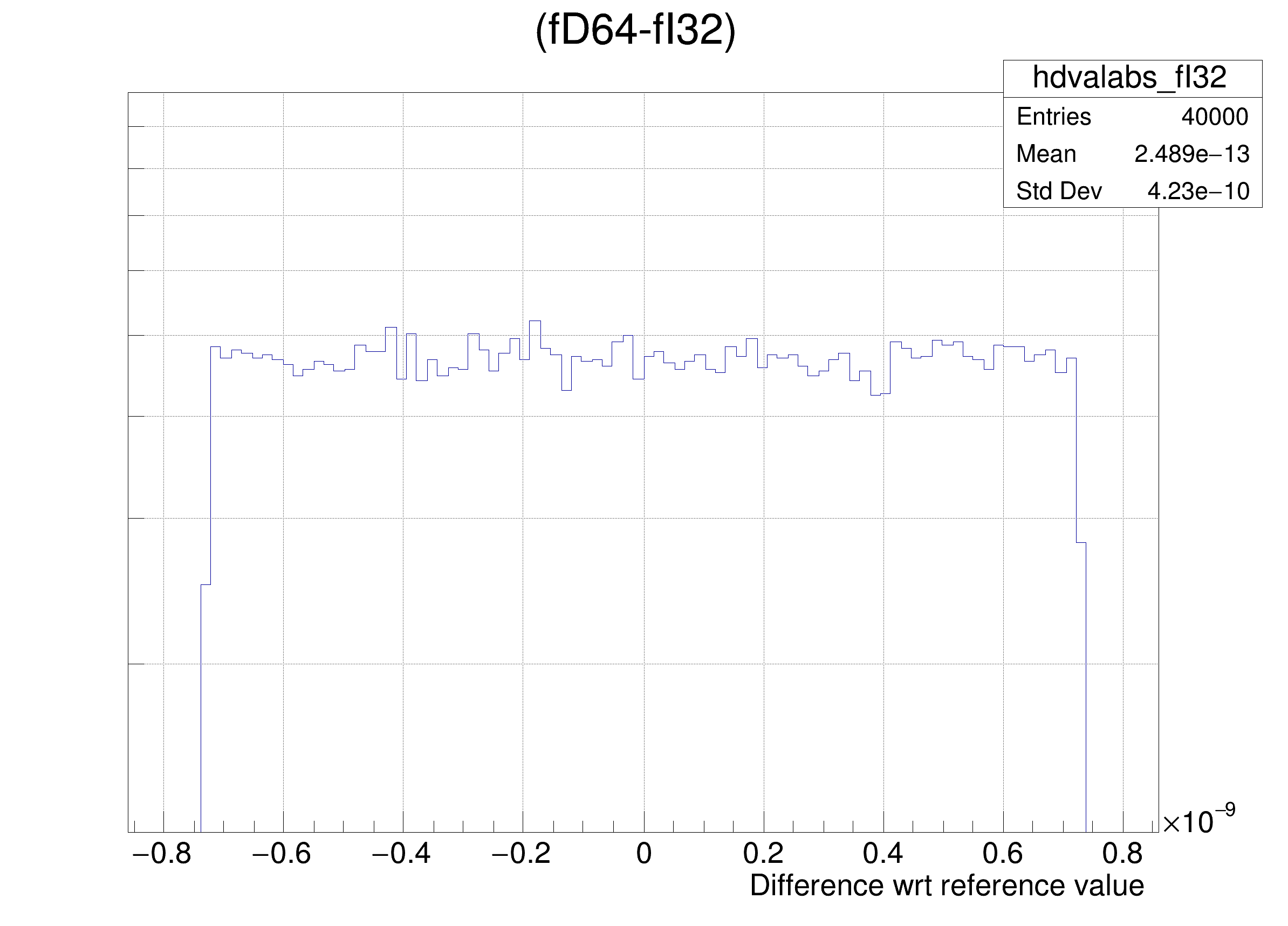
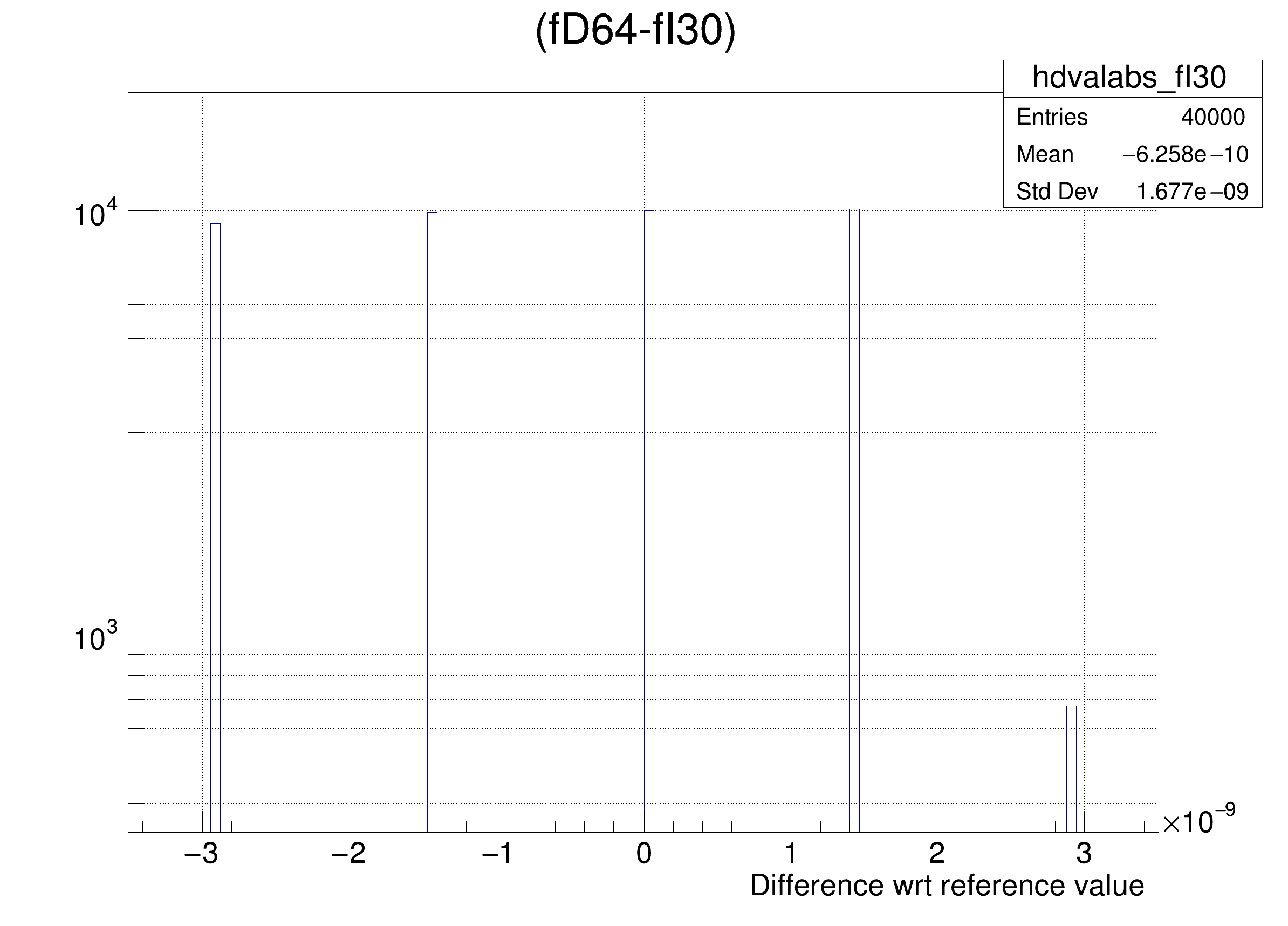
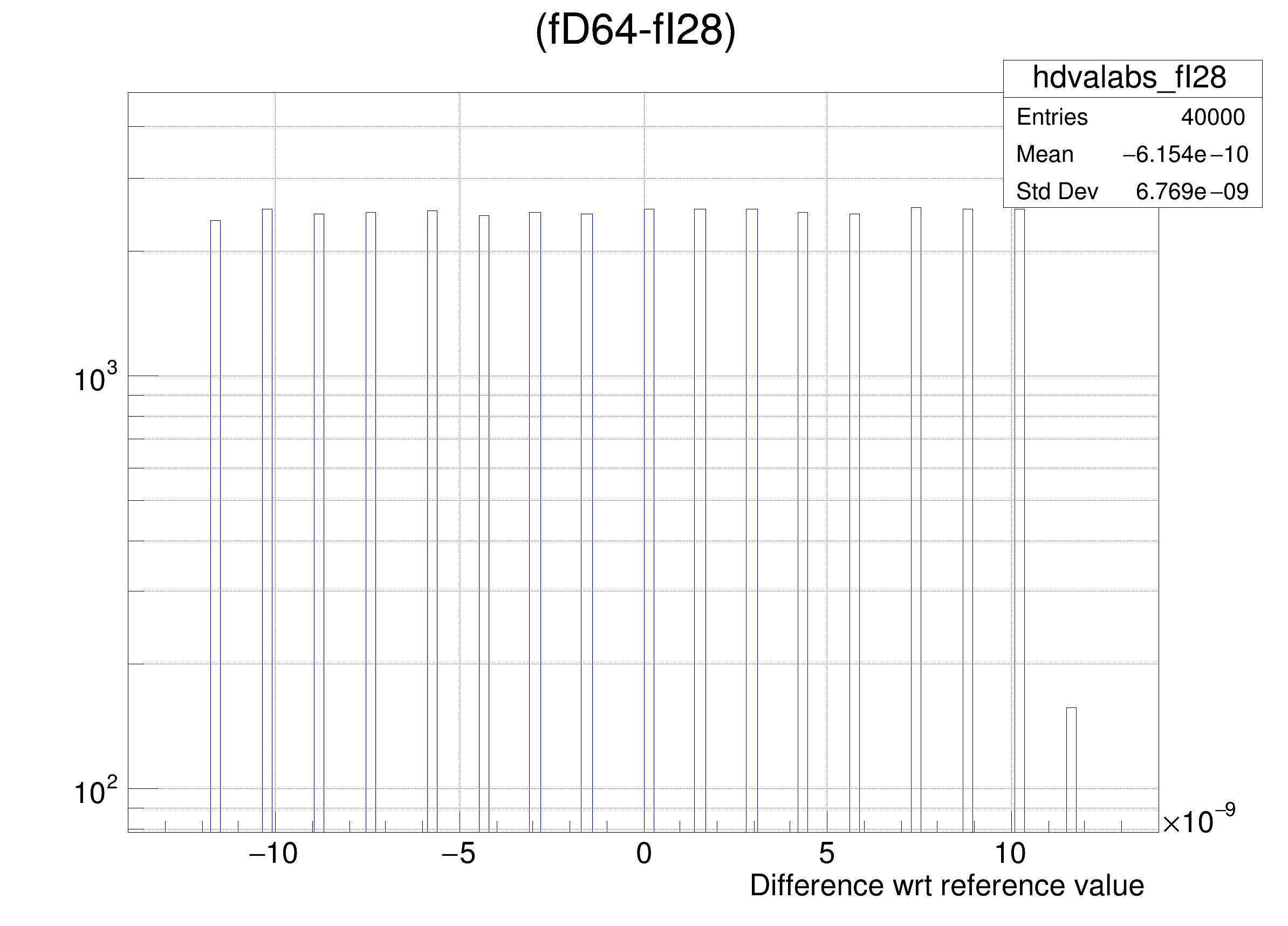
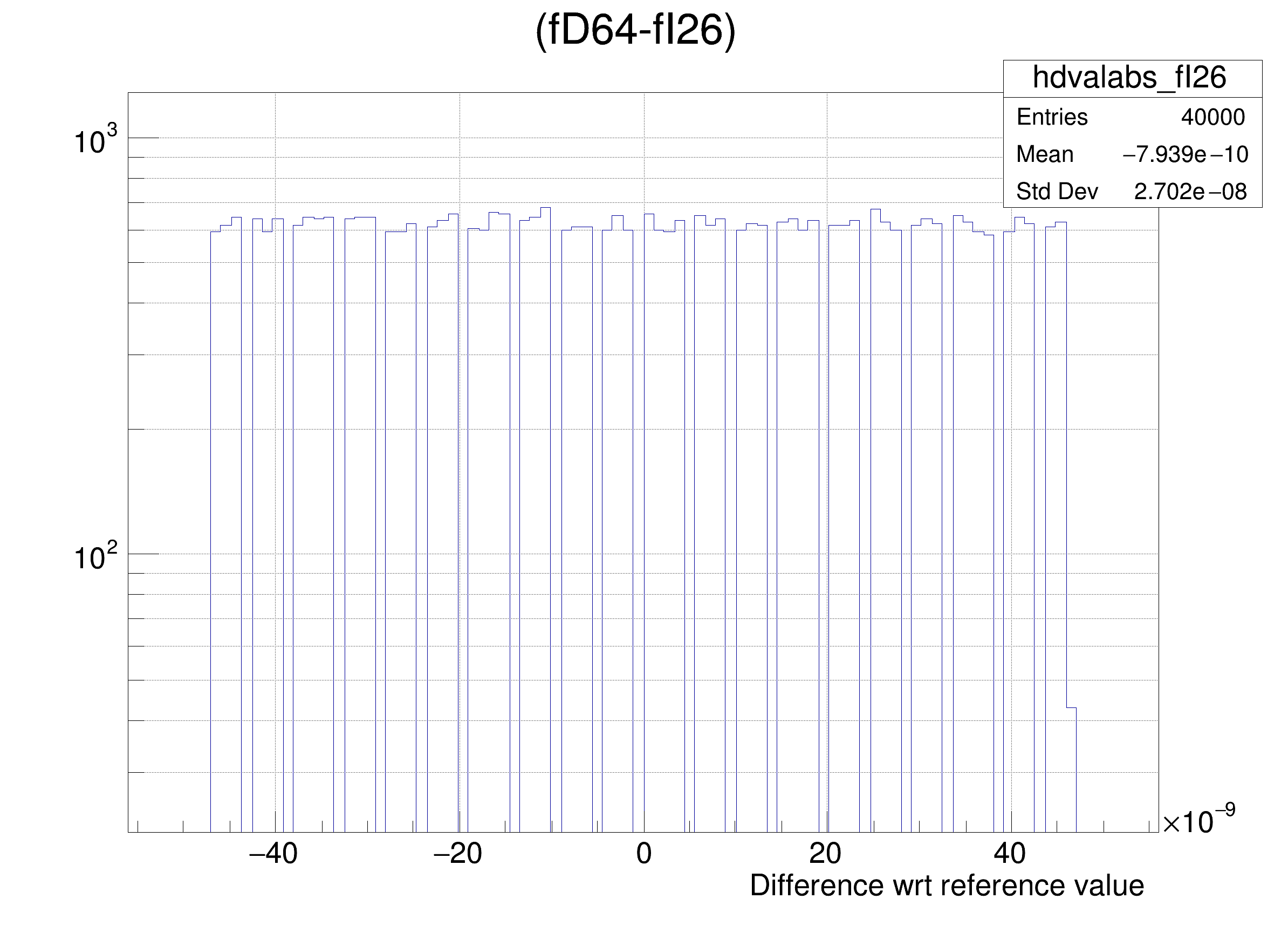
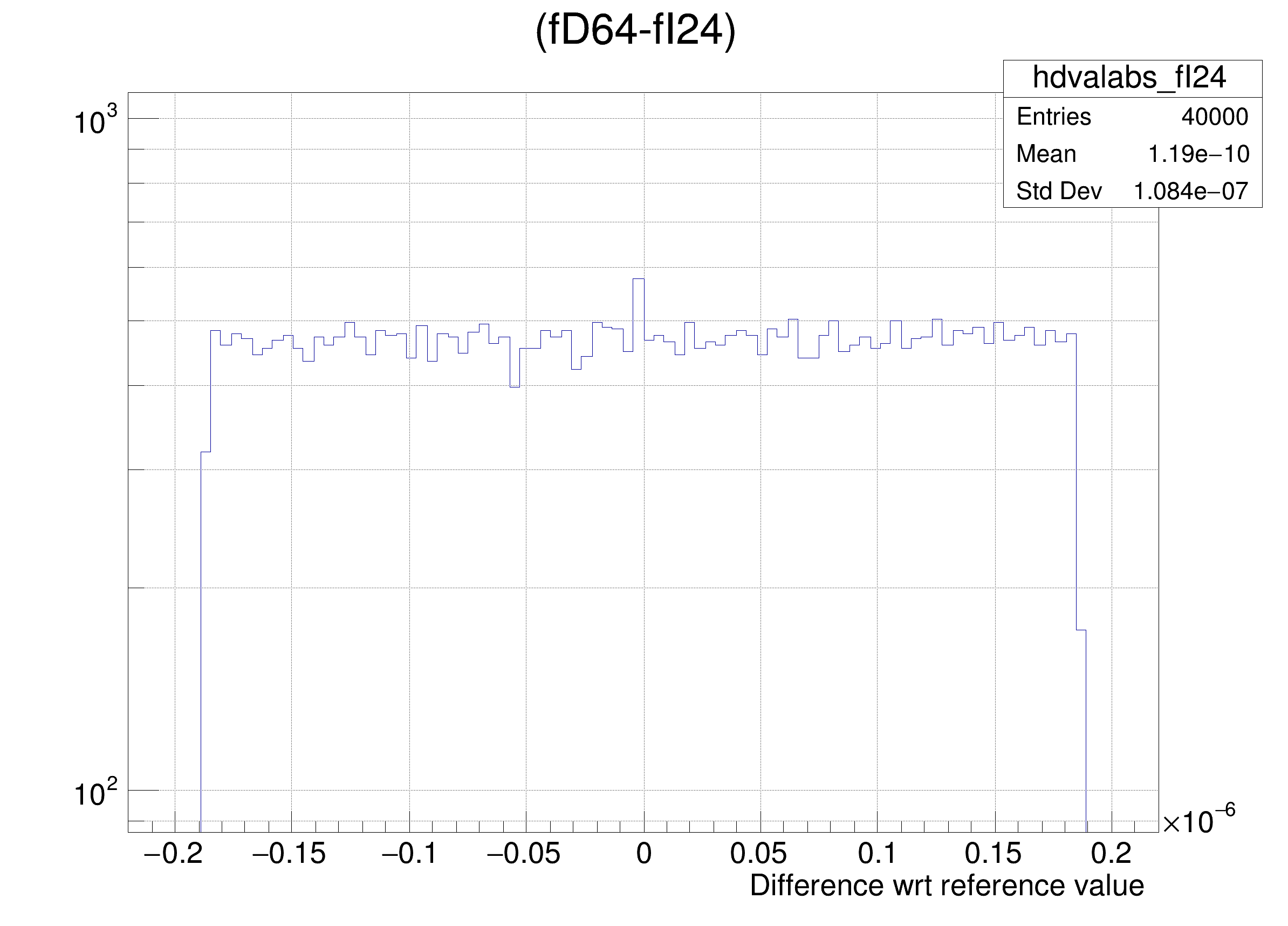
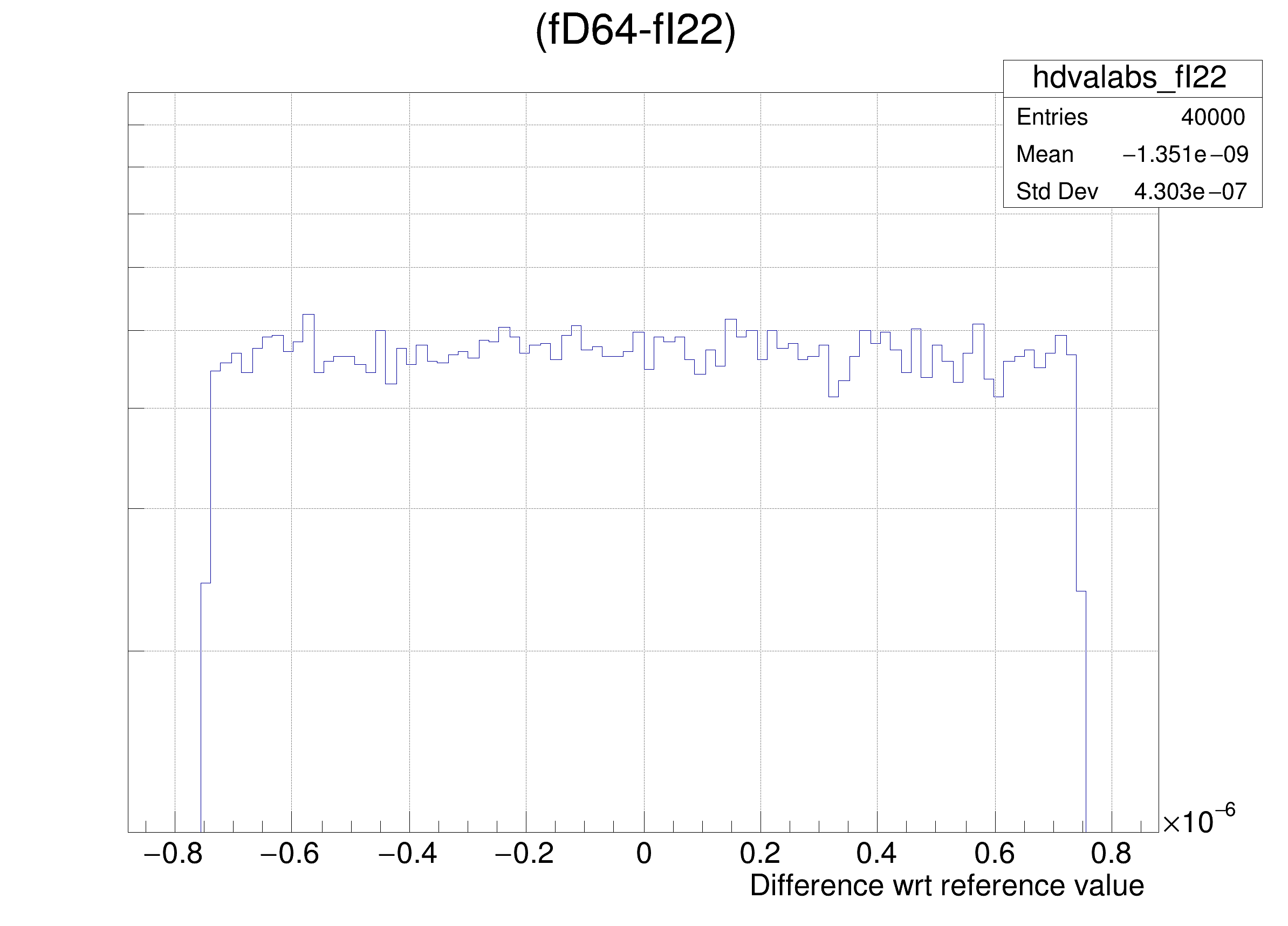
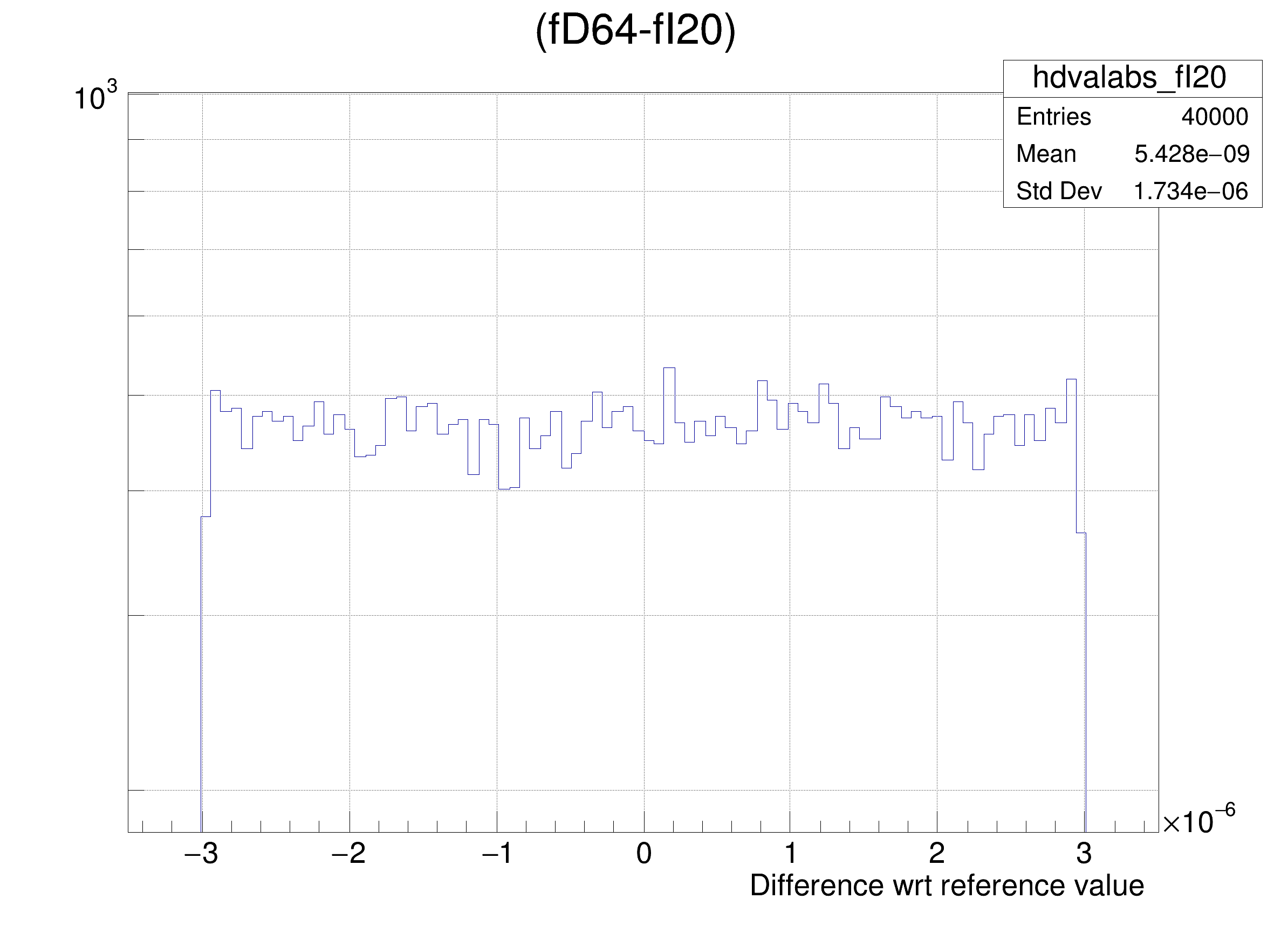
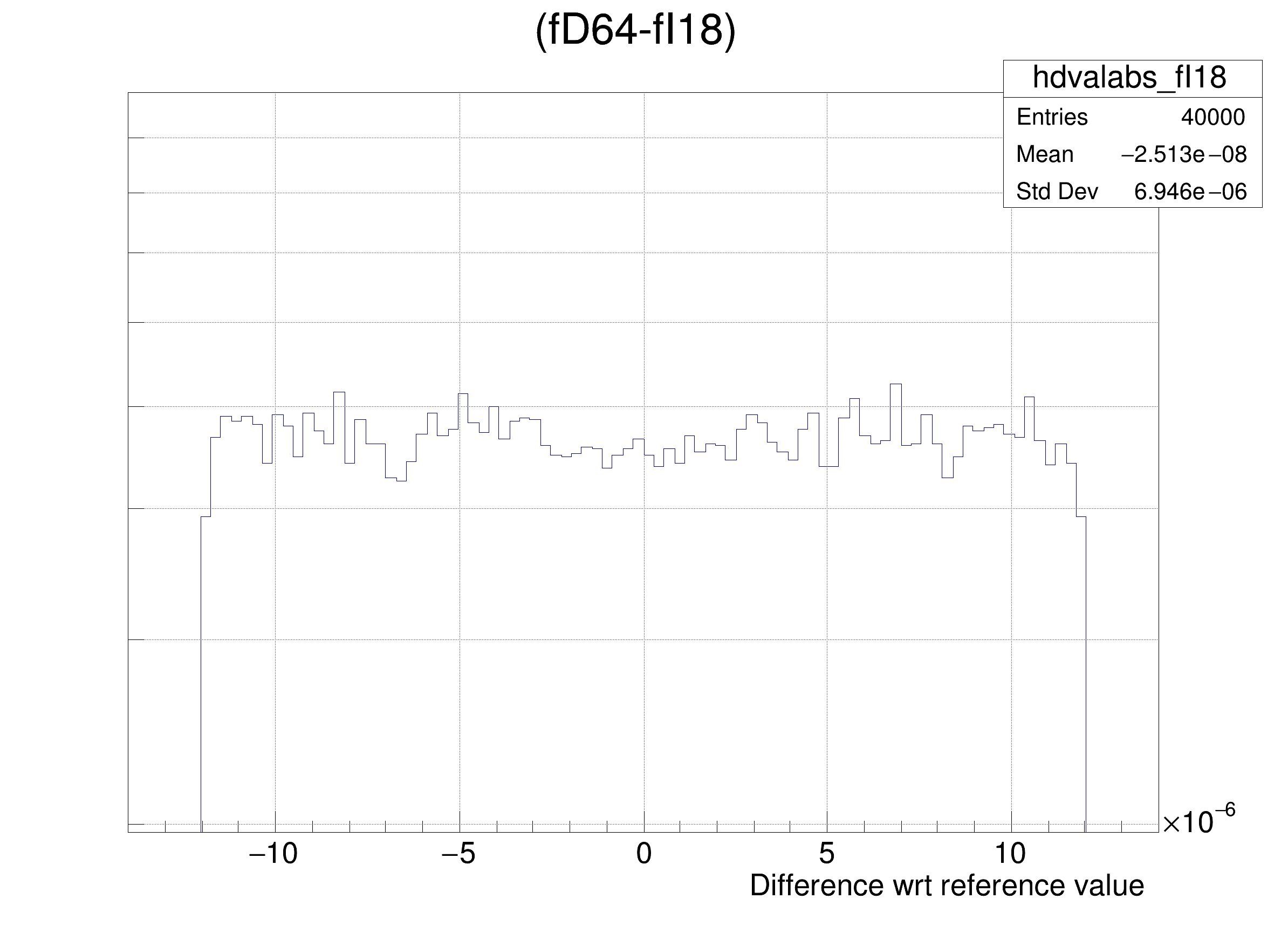
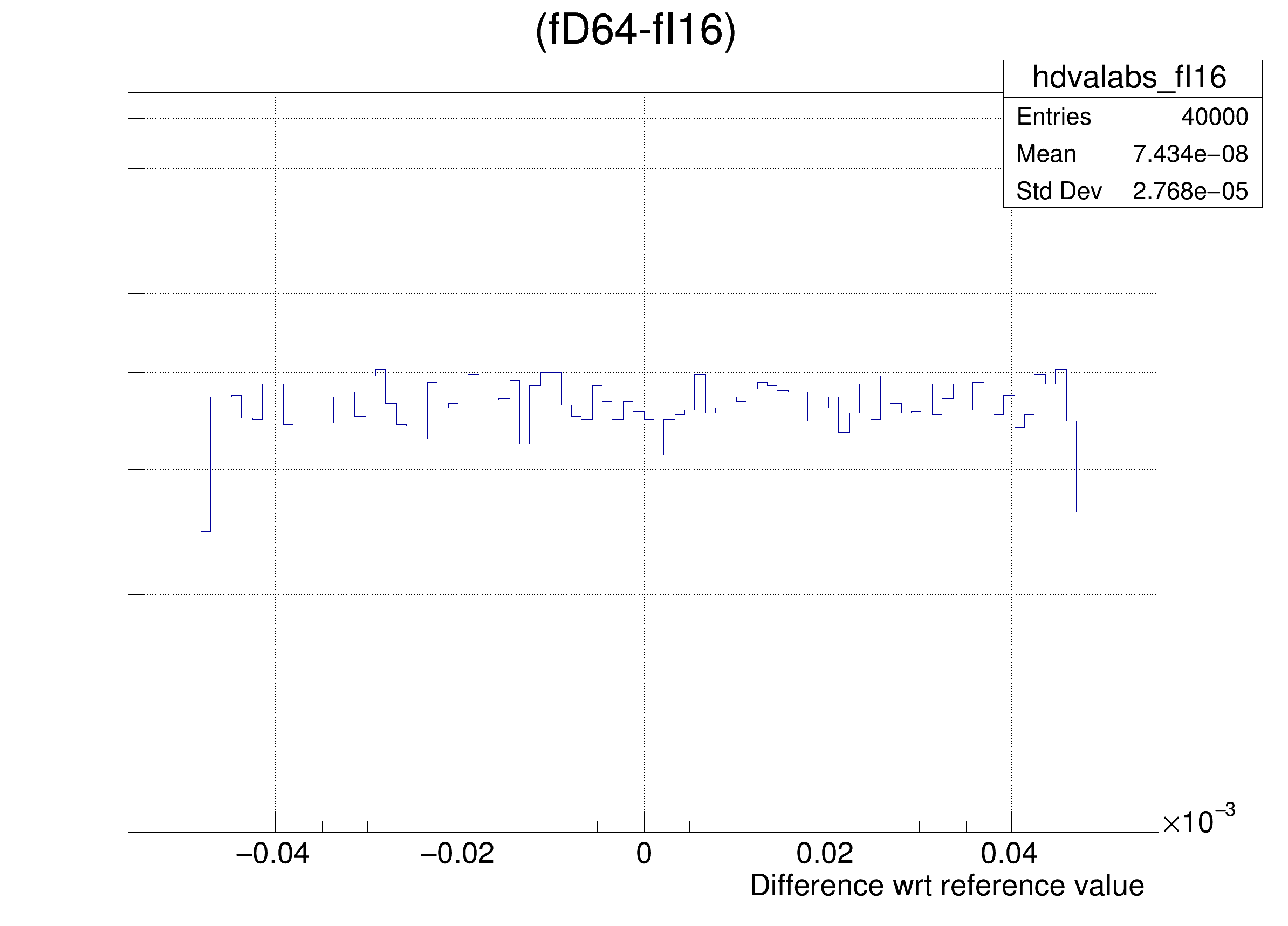
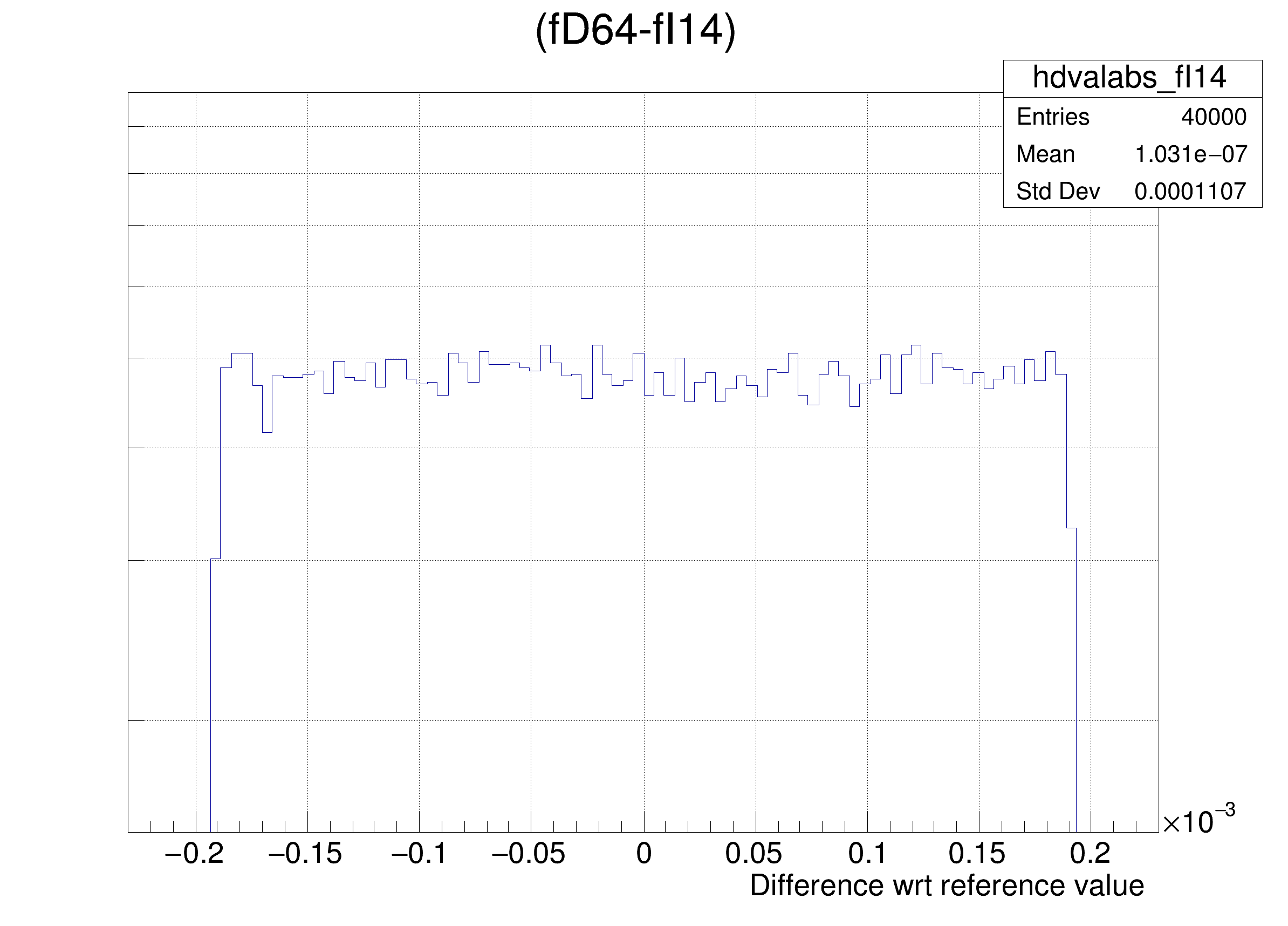
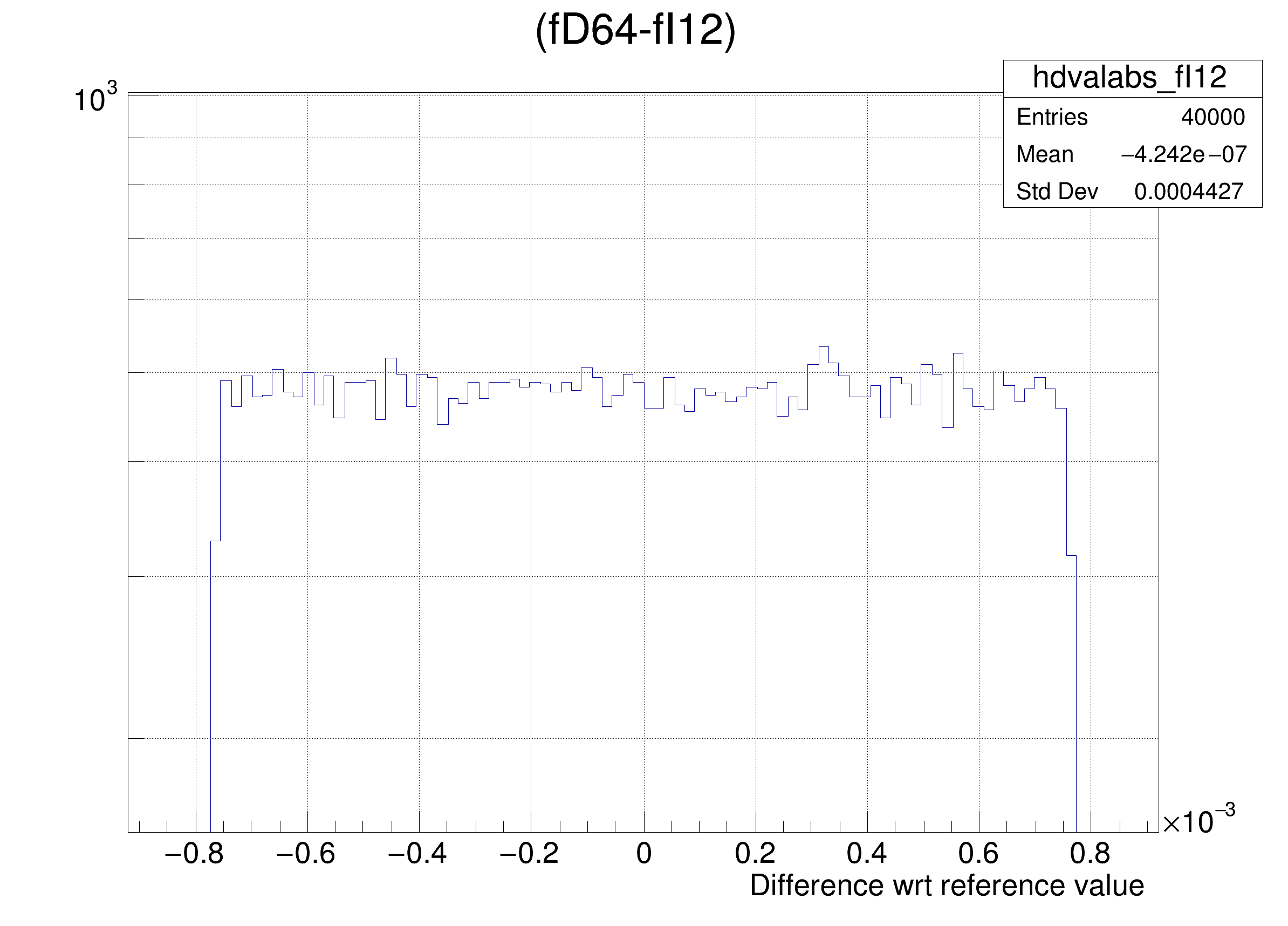
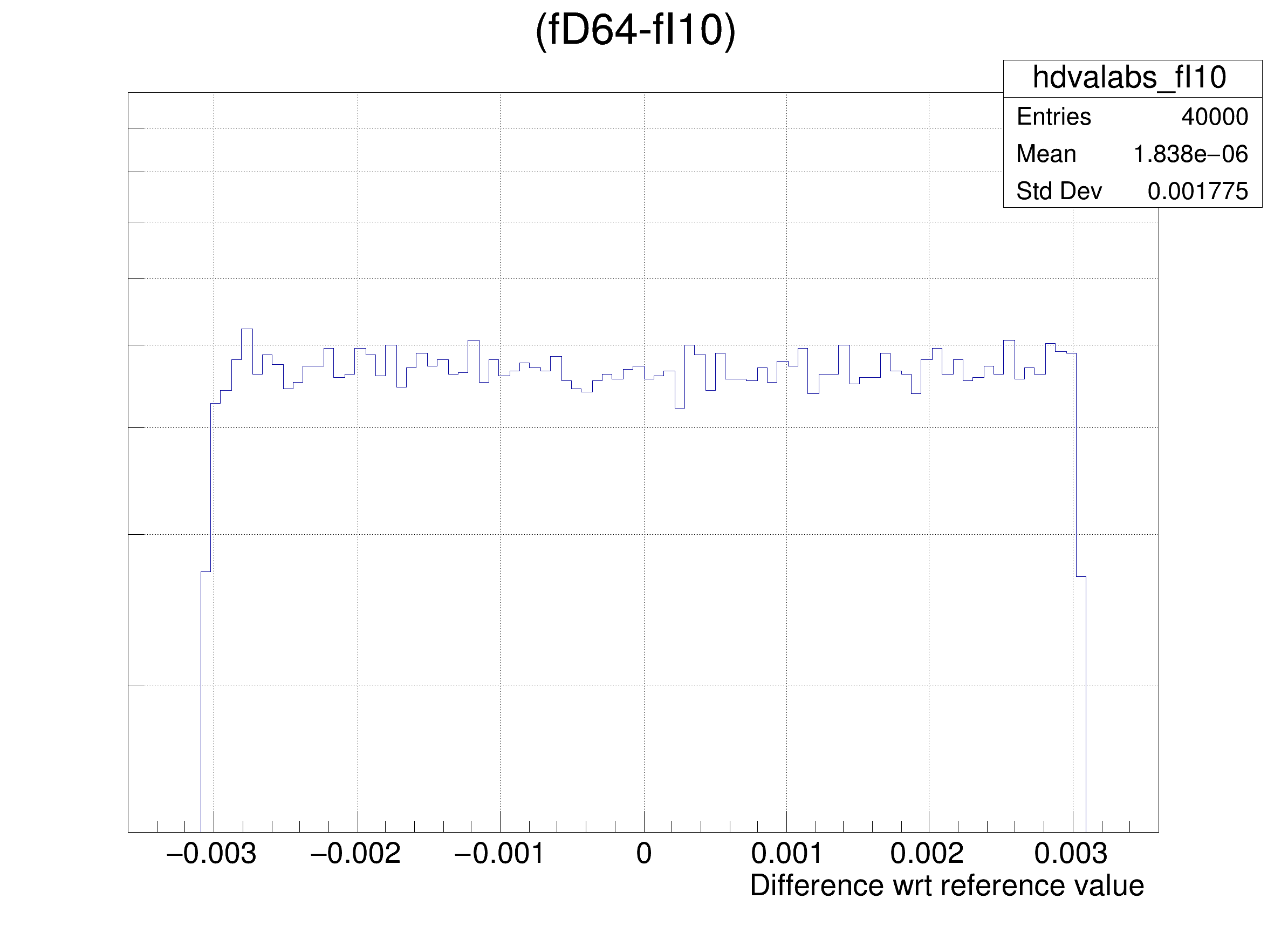
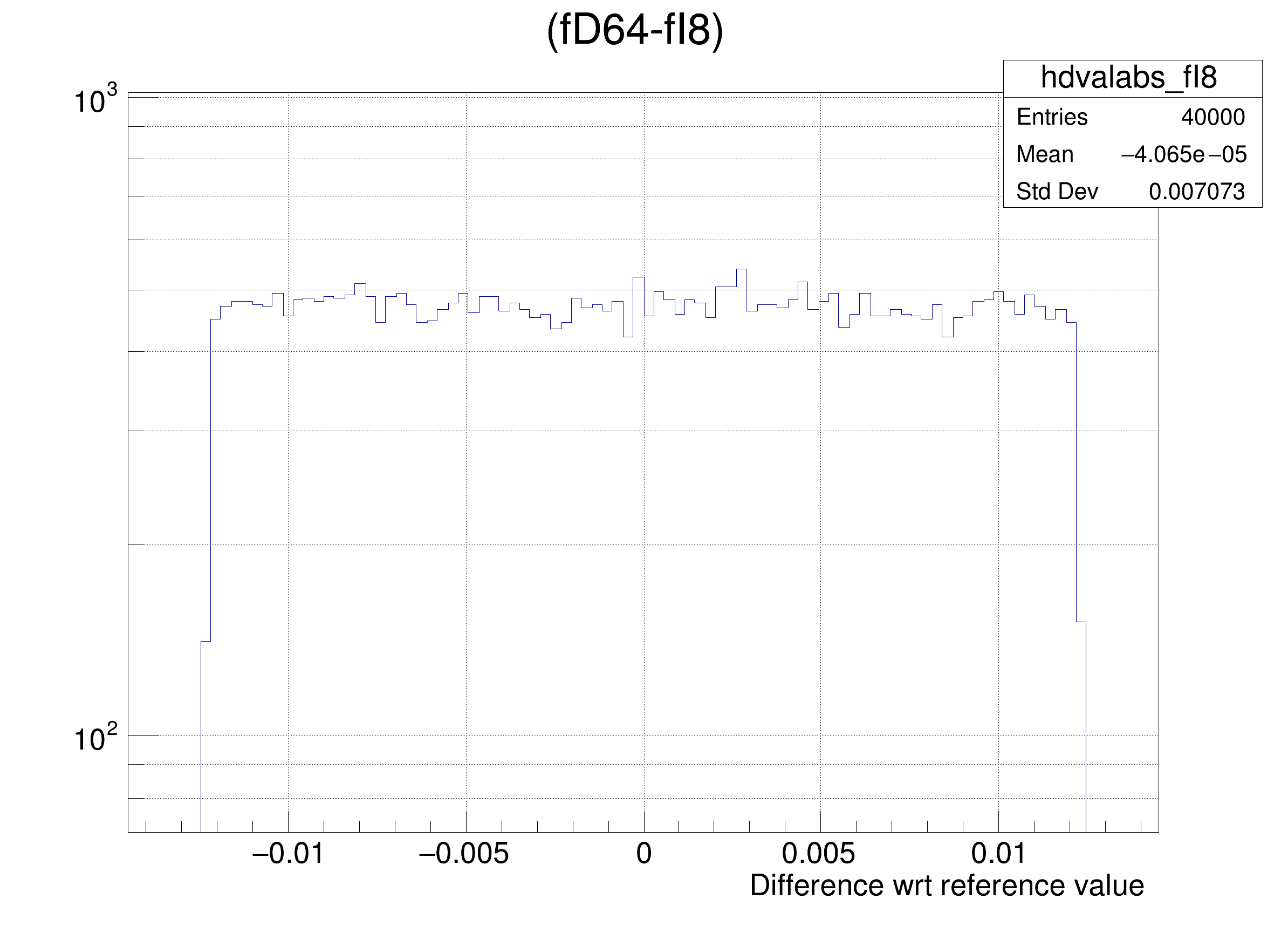
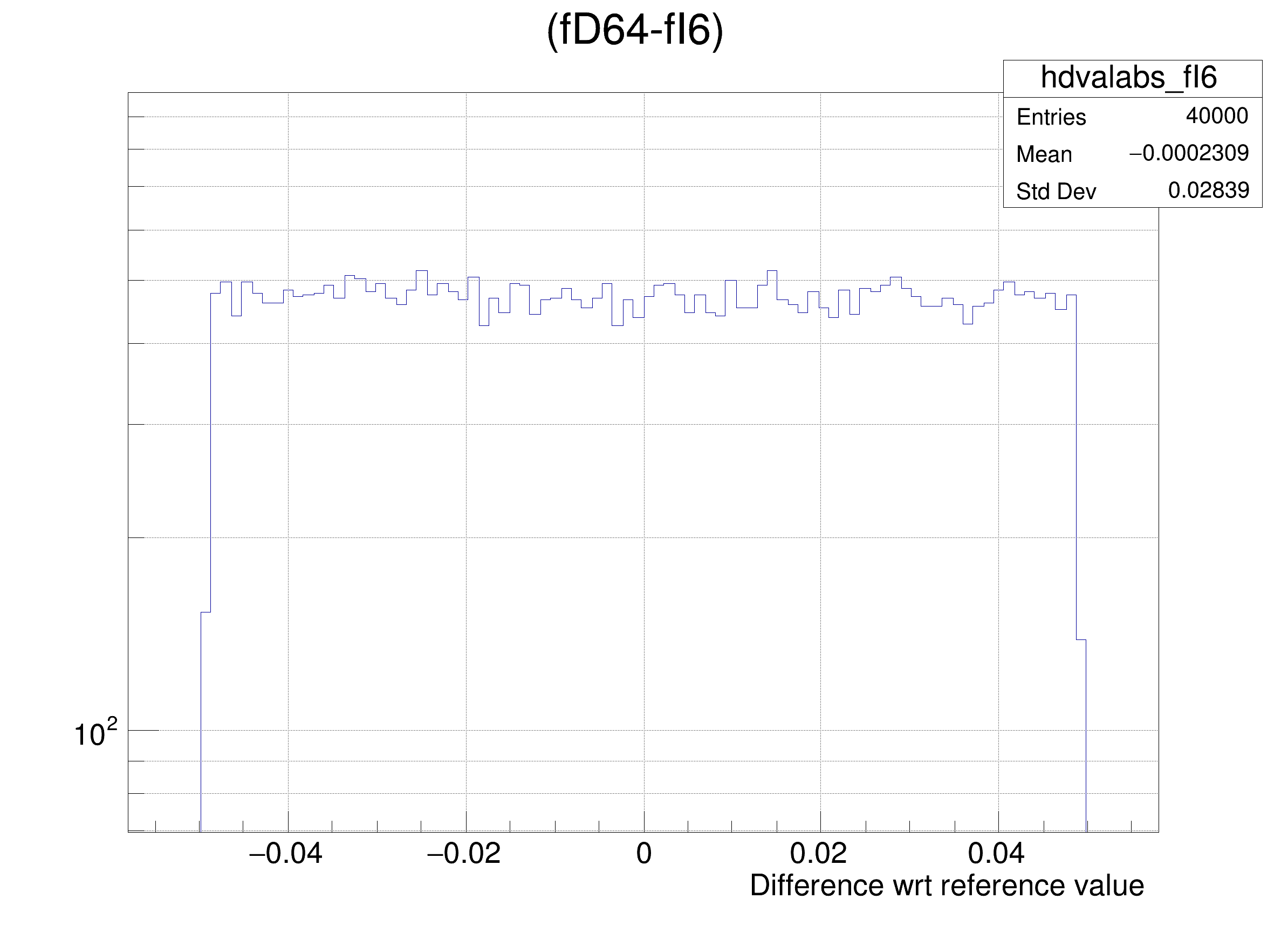
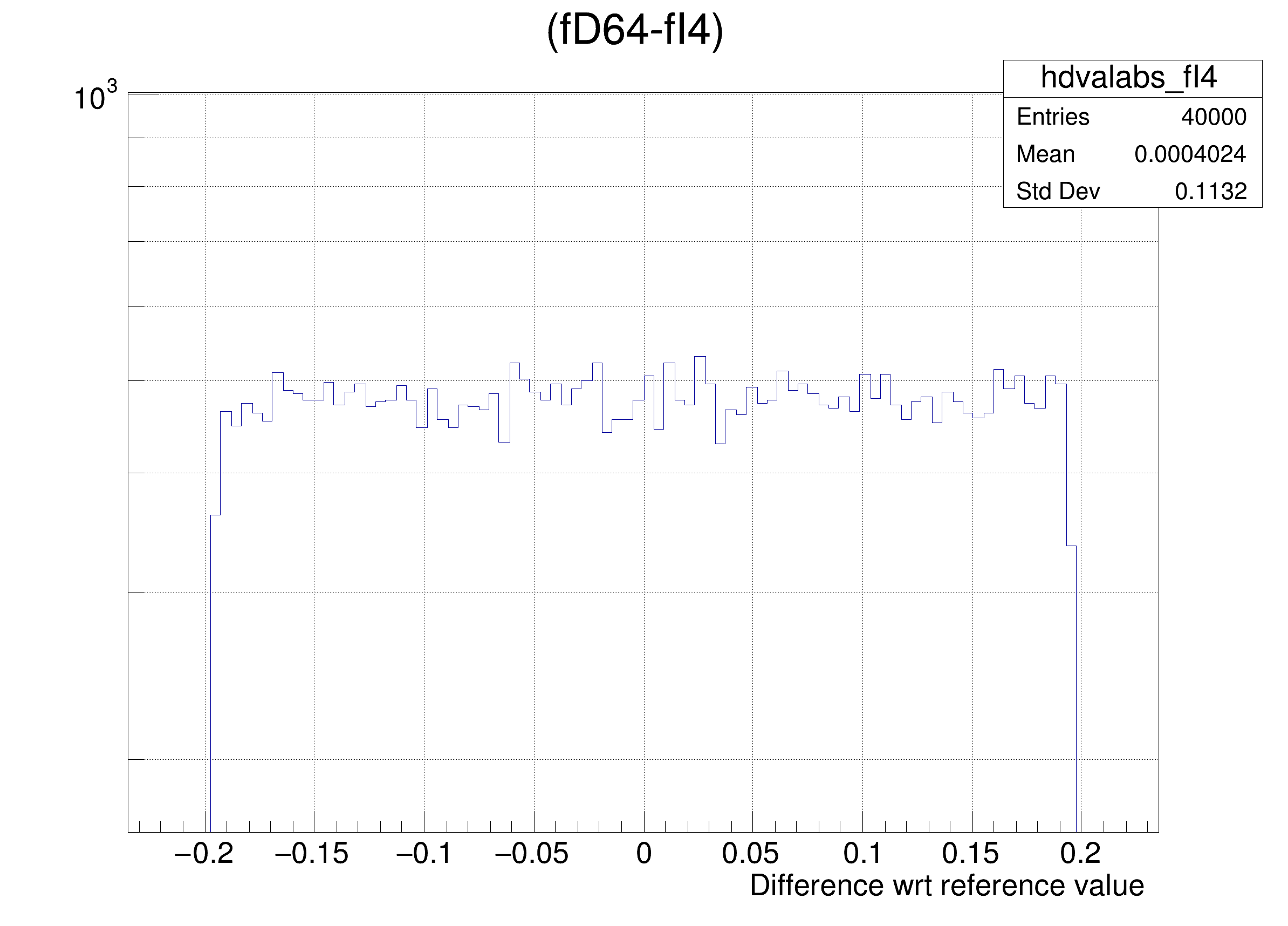
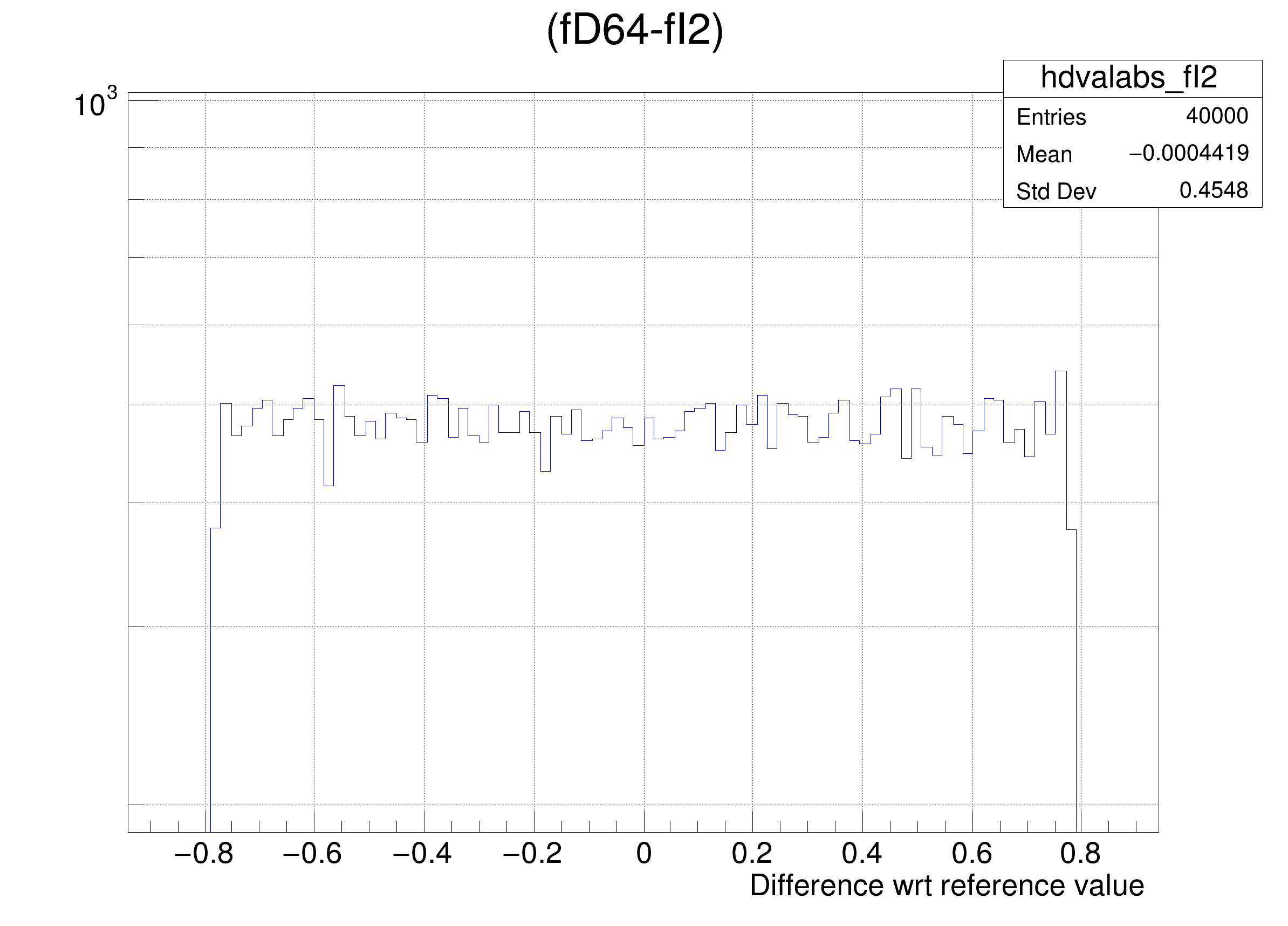
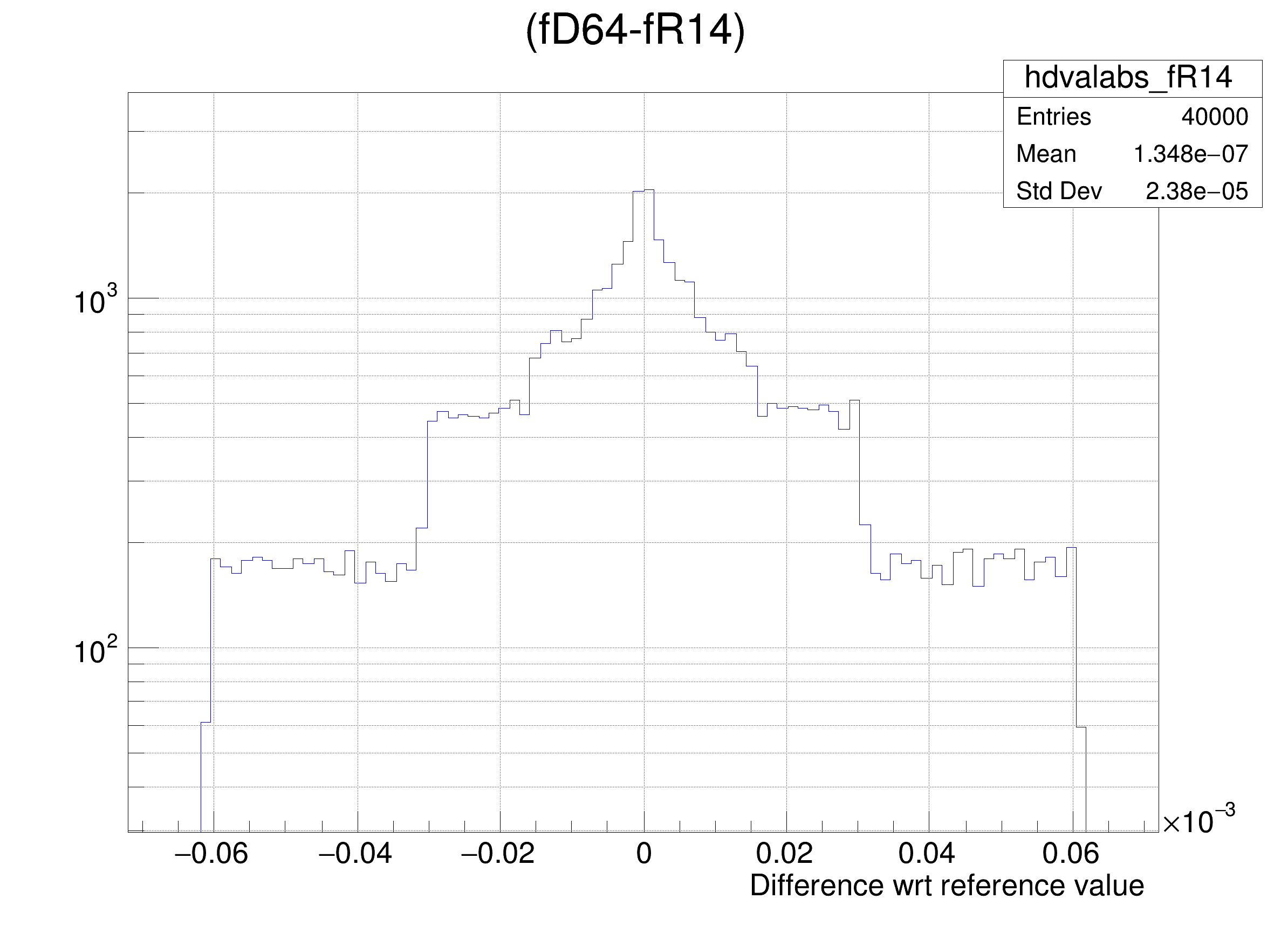
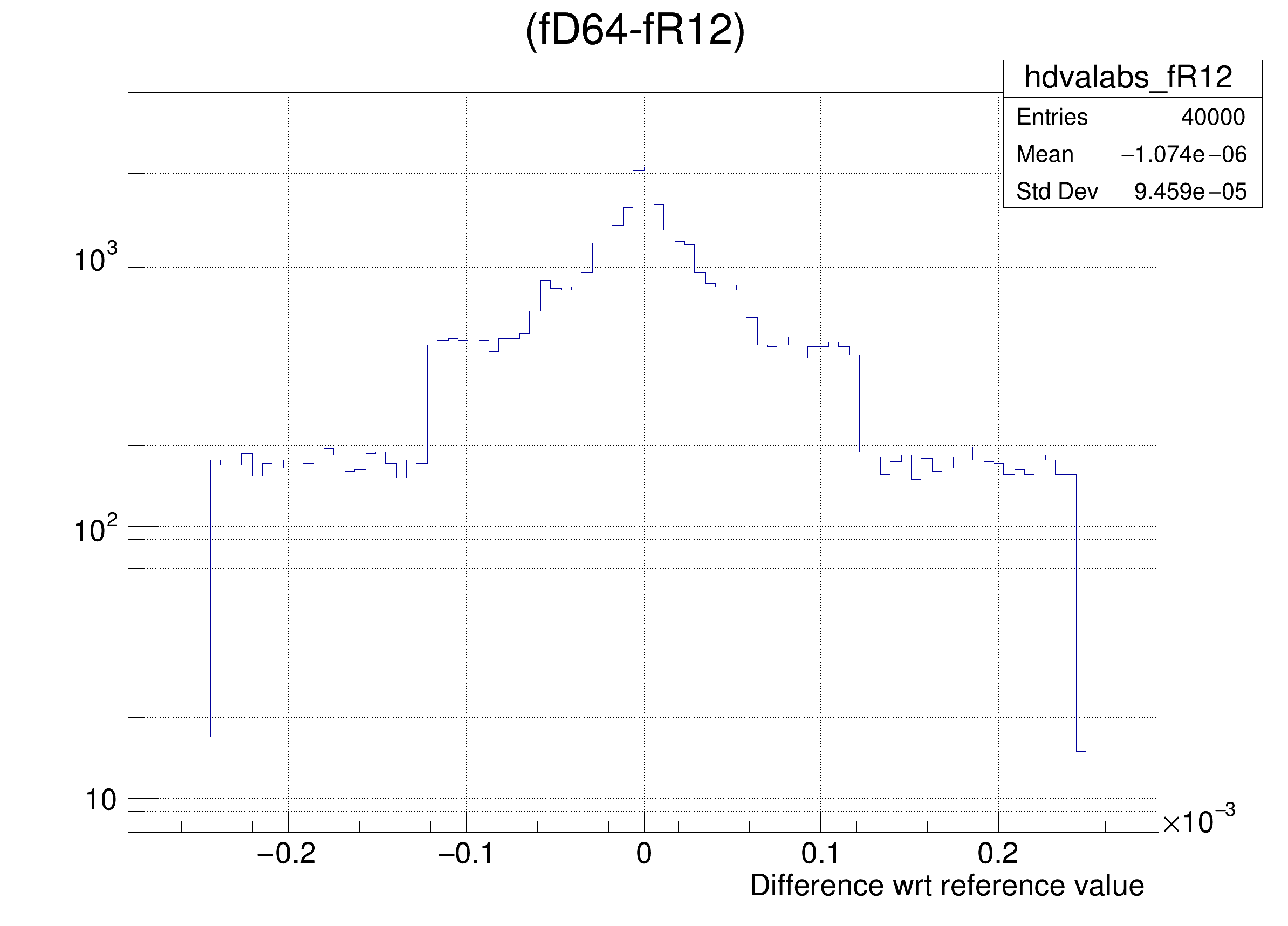
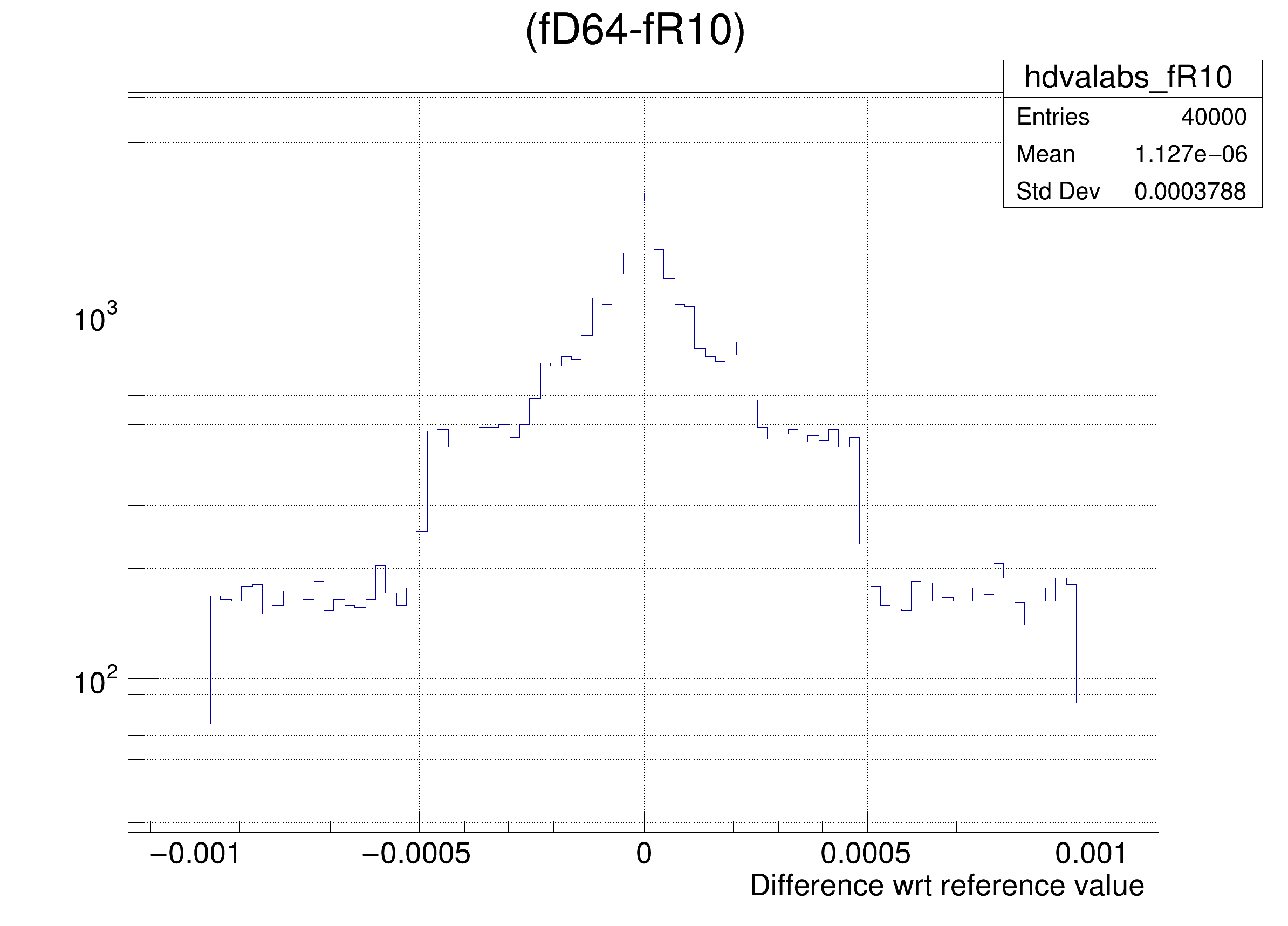
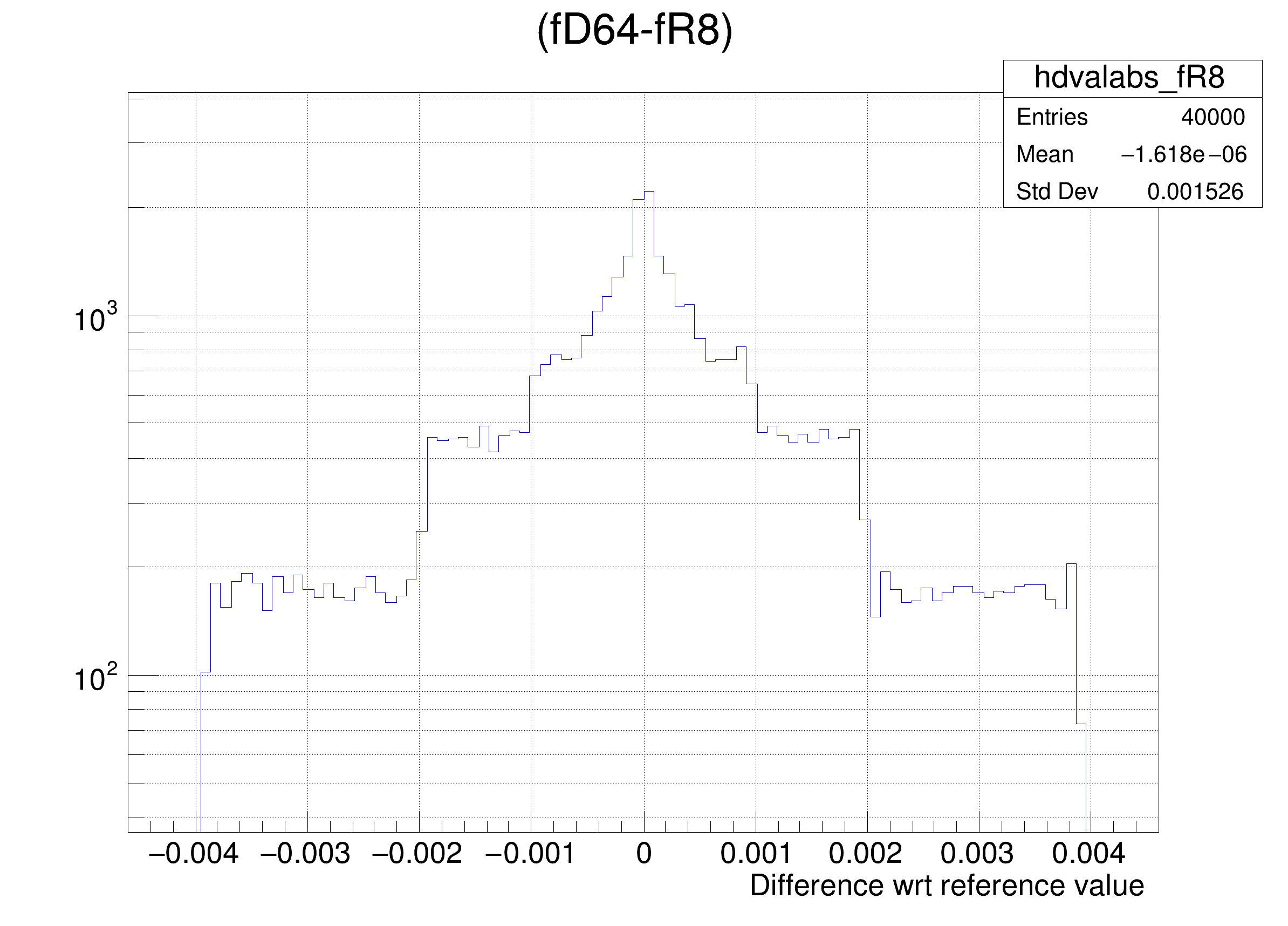
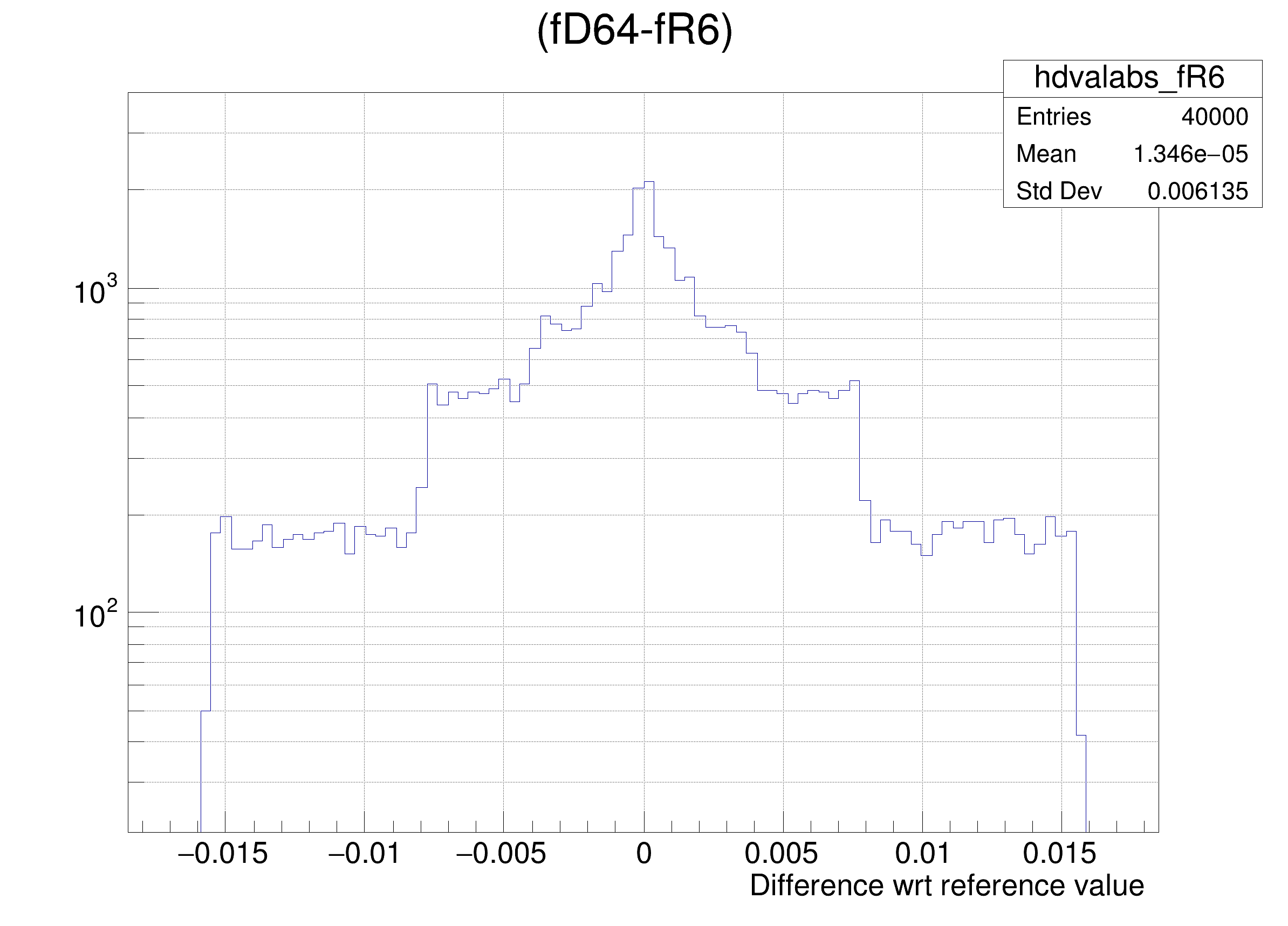
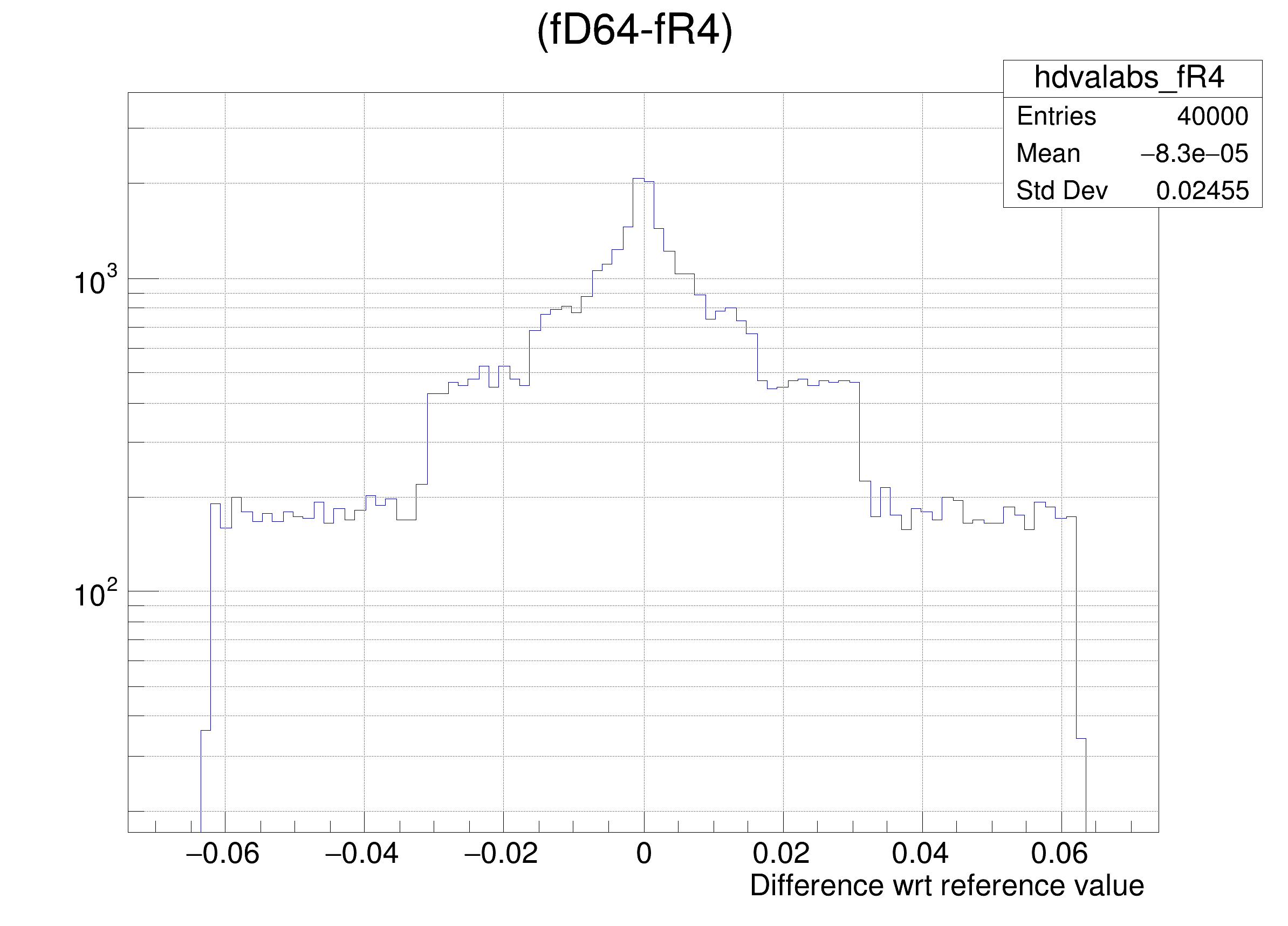
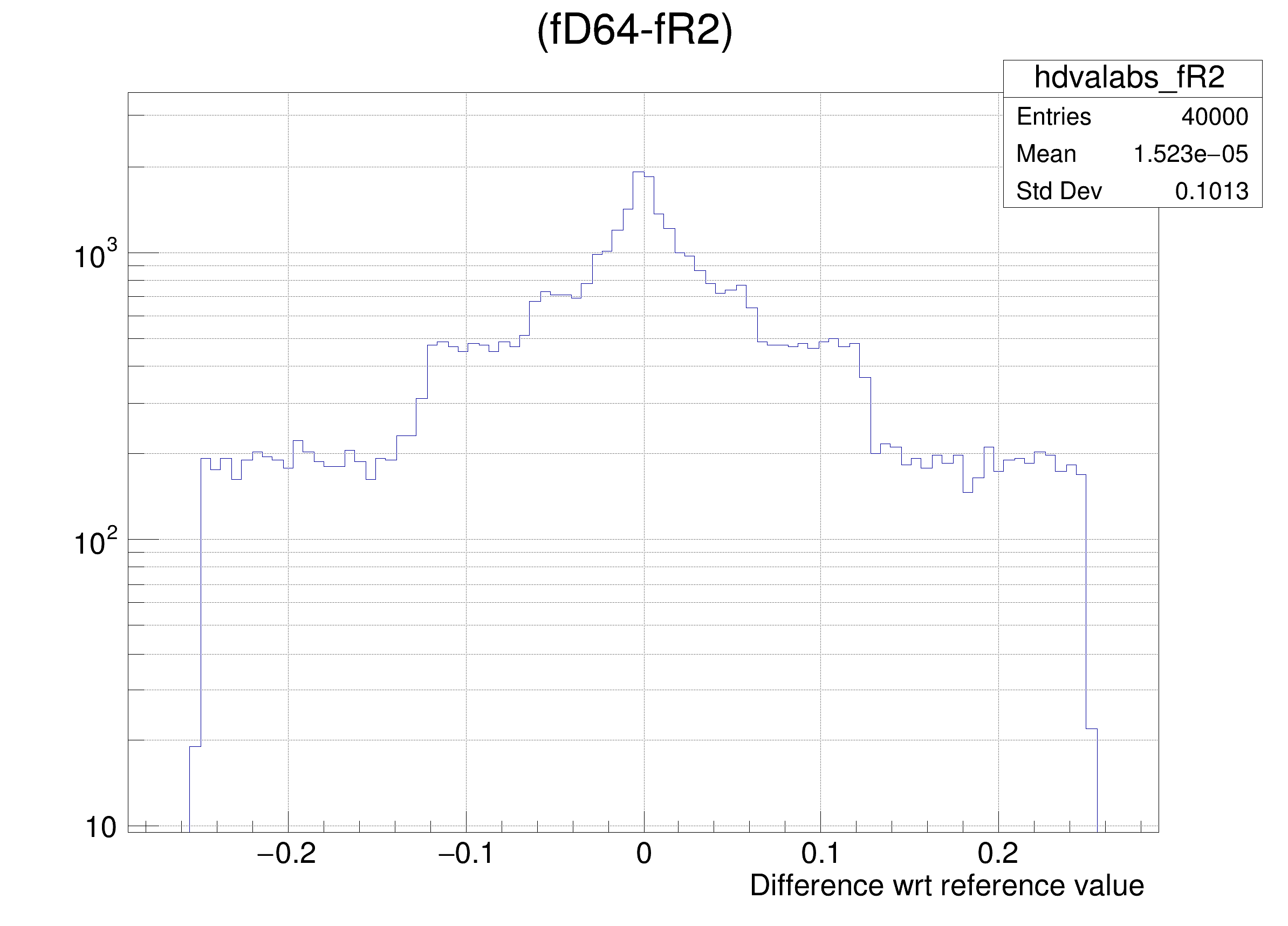
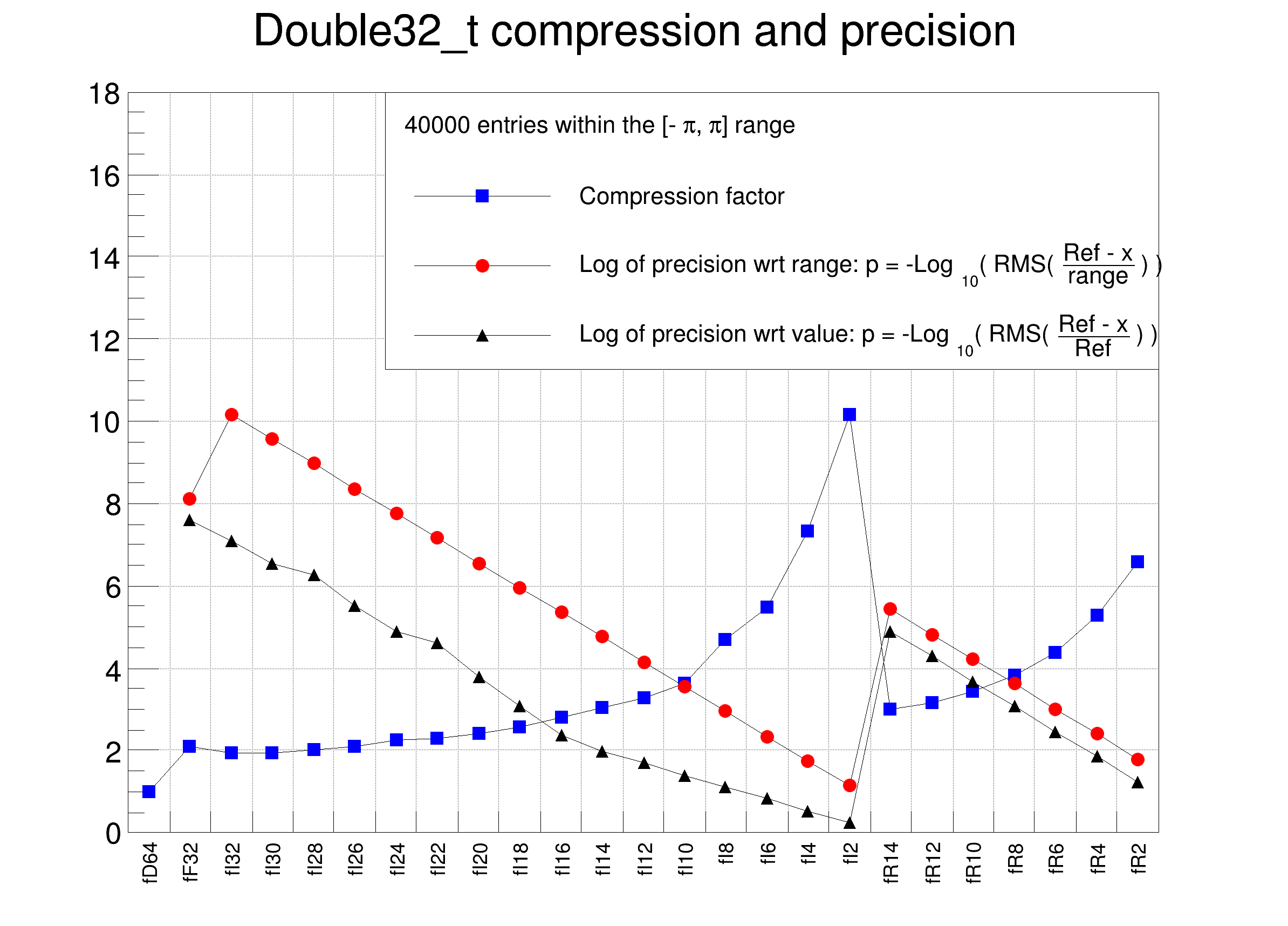
The following cases are supported for streaming a Double32_t type depending on the range declaration in the comment field of the data member:
Case B has more precision than case A: 9 to 10 significative digits and 6 to 7 digits respectively. The range specifier has the general format: [xmin,xmax] or [xmin,xmax,nbits]. Examples
Lets assume an original variable double x. When using the format [0,0,8] (i.e. range not specified) you get the best relative precision when storing and reading back the truncated x, say xt. The variance of (x-xt)/x will be better than when specifying a range for the same number of bits. However the precision relative to the range (x-xt)/(xmax-xmin) will be worse, and vice-versa. The format [0,0,8] is also interesting when the range of x is infinite or unknown.
class DemoDouble32 {
private:
public:
DemoDouble32() = default;
{
fD64 = fF32 = fI32 = fI30 = fI28 = fI26 = fI24 = fI22 = fI20 = fI18 = fI16 = fI14 = fI12 = fI10 = fI8 = fI6 =
fI4 = fI2 = fR14 = fR12 = fR10 = fR8 = fR6 = fR4 = fR2 = ref;
}
};
void double32()
{
const auto nEntries = 40000;
DemoDouble32 demoInstance;
auto demoInstanceBranch =
tree.Branch(
"d",
"DemoDouble32", &demoInstance, 4000);
}
auto branches = demoInstanceBranch->GetListOfBranches();
const auto nb = branches->GetEntries();
auto br =
static_cast<TBranch *
>(branches->At(0));
auto h =
new TH1F(
"h",
"Double32_t compression and precision", nb, 0, nb);
gcx->SetName("gcx");
gcx->SetMarkerColor(
kBlue);
gdrange->SetName("gdrange");
gdrange->SetMarkerColor(
kRed);
gdval->SetName("gdval");
gdval->SetMarkerColor(
kBlack);
auto br =
static_cast<TBranch *
>(branches->At(i));
h->GetXaxis()->SetBinLabel(i + 1, brName);
const auto cx =
double(zip64) / br->GetZipBytes();
gcx->SetPoint(i, i + 0.5, cx);
if (i == 0 ) continue;
gdrange->SetPoint(i-1, i + 0.5, drange);
tree.Draw(
Form(
"(fD64-%s)/fD64", brName),
"",
"goff");
gdval->SetPoint(i-1, i + 0.5, dval);
tree.Draw(
Form(
"(fD64-%s) >> hdvalabs_%s", brName, brName),
"",
"goff");
auto c =
new TCanvas(brName, brName, 800, 600);
hdval->DrawClone();
}
h->GetXaxis()->LabelsOption(
"v");
gcx->Draw("lp");
gdrange->Draw("lp");
gdval->Draw("lp");
auto legend =
new TLegend(0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 0.9);
legend->SetHeader(
Form(
"%d entries within the [-#pi, #pi] range", nEntries));
legend->AddEntry(gcx, "Compression factor", "lp");
legend->AddEntry(gdrange, "Log of precision wrt range: p = -Log_{10}( RMS( #frac{Ref - x}{range} ) ) ", "lp");
legend->AddEntry(gdval, "Log of precision wrt value: p = -Log_{10}( RMS( #frac{Ref - x}{Ref} ) ) ", "lp");
legend->Draw();
}
char * Form(const char *fmt,...)
A TTree is a list of TBranches.
Long64_t GetZipBytes(Option_t *option="") const
Return total number of zip bytes in the branch if option ="*" includes all sub-branches of this branc...
static TFile * Open(const char *name, Option_t *option="", const char *ftitle="", Int_t compress=ROOT::RCompressionSetting::EDefaults::kUseCompiledDefault, Int_t netopt=0)
Create / open a file.
A TGraph is an object made of two arrays X and Y with npoints each.
1-D histogram with a float per channel (see TH1 documentation)}
TAxis * GetXaxis()
Get the behaviour adopted by the object about the statoverflows. See EStatOverflows for more informat...
This class displays a legend box (TPaveText) containing several legend entries.
virtual void SetTitle(const char *title="")
Set the title of the TNamed.
virtual const char * GetName() const
Returns name of object.
Random number generator class based on M.
A TTree represents a columnar dataset.
tbb::task_arena is an alias of tbb::interface7::task_arena, which doesn't allow to forward declare tb...
Short_t Max(Short_t a, Short_t b)
Double_t RMS(Long64_t n, const T *a, const Double_t *w=0)
Return the Standard Deviation of an array a with length n.
Double_t Log10(Double_t x)

 Tutorial illustrating use and precision of the Double32_t data type You should run this tutorial with ACLIC: a dictionary will be automatically created.
Tutorial illustrating use and precision of the Double32_t data type You should run this tutorial with ACLIC: a dictionary will be automatically created.