library: libTMVA
#include "MethodCFMlpANN.h" |
TMVA::MethodCFMlpANN
class description - header file - source file - inheritance tree (.pdf)
private:
Double_t EvalANN(vector<Double_t>*, Bool_t& isOK)
void InitCFMlpANN()
void NN_ava(Double_t*)
Double_t NN_fonc(Int_t, Double_t) const
protected:
virtual Int_t DataInterface(Double_t*, Double_t*, Int_t*, Int_t*, Int_t*, Int_t*, Double_t*, Int_t*, Int_t*)
virtual void WriteNNWeightsToFile(Int_t, Int_t, Double_t*, Double_t*, Int_t, Int_t*, Double_t*, Double_t*, Double_t*)
public:
MethodCFMlpANN(TString jobName, vector<TString>* theVariables, TTree* theTree = 0, TString theOption = 3000:N-1:N-2, TDirectory* theTargetDir = 0)
MethodCFMlpANN(vector<TString>* theVariables, TString theWeightFile, TDirectory* theTargetDir = NULL)
MethodCFMlpANN(const TMVA::MethodCFMlpANN&)
virtual ~MethodCFMlpANN()
static TClass* Class()
Int_t GetClass(Int_t ivar) const
Double_t GetData(Int_t isel, Int_t ivar) const
virtual Double_t GetMvaValue(TMVA::Event* e)
virtual TClass* IsA() const
TMVA::MethodCFMlpANN& operator=(const TMVA::MethodCFMlpANN&)
virtual void ReadWeightsFromFile()
virtual void ShowMembers(TMemberInspector& insp, char* parent)
virtual void Streamer(TBuffer& b)
void StreamerNVirtual(TBuffer& b)
static TMVA::MethodCFMlpANN* This()
virtual void Train()
virtual void WriteHistosToFile()
virtual void WriteWeightsToFile()
private:
static TMVA::MethodCFMlpANN* fgThis
TMatrix* fData the (data,var) string
vector<Int_t>* fClass the event class (1=signal, 2=background)
Int_t fNevt number of training events
Int_t fNsig number of signal events
Int_t fNbgd number of background
Int_t fNlayers number of layers (including input and output layers)
Int_t fNcycles number of training cycles
Int_t* fNodes number of nodes per layer
Double_t* fXmaxNN maximum values of input variables
Double_t* fXminNN minimum values of input variables
Int_t fLayermNN number of layers (including input and output layers)
Int_t* fNeuronNN nodes per layer
Double_t*** fWNN weights
Double_t** fWwNN weights
Double_t** fYNN weights
Double_t* fTempNN temperature (used in activation function)
_______________________________________________________________________
Interface to Clermond-Ferrand artificial neural network
The CFMlpANN belong to the class of Multilayer Perceptrons (MLP), which are
feed-forward networks according to the following propagation schema:
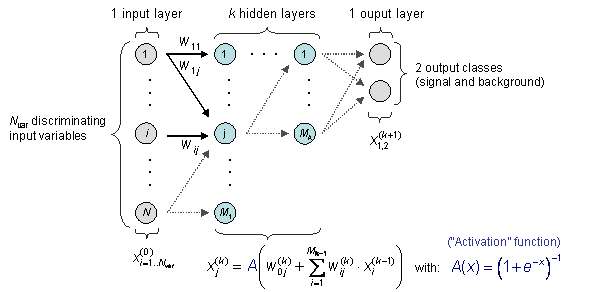
The input layer contains as many neurons as input variables used in the MVA.
The output layer contains two neurons for the signal and background
event classes. In between the input and output layers are a variable number
of
k hidden layers with arbitrary numbers of neurons. (While the
structure of the input and output layers is determined by the problem, the
hidden layers can be configured by the user through the option string
of the method booking.)
As indicated in the sketch, all neuron inputs to a layer are linear
combinations of the neuron output of the previous layer. The transfer
from input to output within a neuron is performed by means of an "activation
function". In general, the activation function of a neuron can be
zero (deactivated), one (linear), or non-linear. The above example uses
a sigmoid activation function. The transfer function of the output layer
is usually linear. As a consequence: an ANN without hidden layer should
give identical discrimination power as a linear discriminant analysis (Fisher).
In case of one hidden layer, the ANN computes a linear combination of
sigmoid.
The learning method used by the CFMlpANN is only stochastic.
_______________________________________________________________________
MethodCFMlpANN( TString jobName, vector<TString>* theVariables, TTree* theTree, TString theOption, TDirectory* theTargetDir )
standard constructor
option string: "n_training_cycles:n_hidden_layers"
default is: n_training_cycles = 5000, n_layers = 4
* note that the number of hidden layers in the NN is:
n_hidden_layers = n_layers - 2
* since there is one input and one output layer. The number of
nodes (neurons) is predefined to be:
n_nodes[i] = nvars + 1 - i (where i=1..n_layers)
with nvars being the number of variables used in the NN.
Hence, the default case is: n_neurons(layer 1 (input)) : nvars
n_neurons(layer 2 (hidden)): nvars-1
n_neurons(layer 3 (hidden)): nvars-1
n_neurons(layer 4 (out)) : 2
This artificial neural network usually needs a relatively large
number of cycles to converge (8000 and more). Overtraining can
be efficienctly tested by comparing the signal and background
output of the NN for the events that were used for training and
an independent data sample (with equal properties). If the separation
performance is significantly better for the training sample, the
NN interprets statistical effects, and is hence overtrained. In
this case, the number of cycles should be reduced, or the size
of the training sample increased.
void InitCFMlpANN( void )
default initialisation called by all constructors
void Train( void )
calls CFMlpANN training
void WriteHistosToFile( void )
write special monitoring histograms to file - not implemented for CFMlpANN
MethodCFMlpANN* This( void )
static pointer to this object (required for external functions
Author: Andreas Hoecker, Joerg Stelzer, Helge Voss, Kai Voss
Last update: root/tmva $Id: MethodCFMlpANN.cxx,v 1.3 2006/05/23 19:35:06 brun Exp $
Copyright (c) 2005: *
ROOT page - Class index - Class Hierarchy - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
