library: libGraf
#include "TGraphAsymmErrors.h" |
TGraphAsymmErrors
class description - header file - source file - inheritance tree (.pdf)
protected:
virtual Double_t** Allocate(Int_t size)
Double_t Beta_ab(double a, double b, int k, int N) const
Double_t Betai(double a, double b, double x) const
Double_t Brent(double ax, double bx, double cx, double tol, double* xmin) const
virtual void CopyAndRelease(Double_t** newarrays, Int_t ibegin, Int_t iend, Int_t obegin)
virtual Bool_t CopyPoints(Double_t** arrays, Int_t ibegin, Int_t iend, Int_t obegin)
Bool_t CtorAllocate()
virtual void Efficiency(int k, int N, double conflevel, double& mode, double& low, double& high) const
virtual void FillZero(Int_t begin, Int_t end, Bool_t from_ctor = kTRUE)
Double_t Ibetai(double a, double b, double x) const
Double_t Interval(double low) const
Double_t SearchLower(double high, int k, int N, double c) const
Double_t SearchUpper(double low, int k, int N, double c) const
virtual void SwapPoints(Int_t pos1, Int_t pos2)
public:
TGraphAsymmErrors()
TGraphAsymmErrors(Int_t n)
TGraphAsymmErrors(Int_t n, const Float_t* x, const Float_t* y, const Float_t* exl = 0, const Float_t* exh = 0, const Float_t* eyl = 0, const Float_t* eyh = 0)
TGraphAsymmErrors(Int_t n, const Double_t* x, const Double_t* y, const Double_t* exl = 0, const Double_t* exh = 0, const Double_t* eyl = 0, const Double_t* eyh = 0)
TGraphAsymmErrors(const TVectorF& vx, const TVectorF& vy, const TVectorF& vexl, const TVectorF& vexh, const TVectorF& veyl, const TVectorF& veyh)
TGraphAsymmErrors(const TVectorD& vx, const TVectorD& vy, const TVectorD& vexl, const TVectorD& vexh, const TVectorD& veyl, const TVectorD& veyh)
TGraphAsymmErrors(const TGraphAsymmErrors& gr)
TGraphAsymmErrors(const TH1* h)
TGraphAsymmErrors(const TH1* pass, const TH1* total, Option_t* option = "")
virtual ~TGraphAsymmErrors()
virtual void Apply(TF1* f)
virtual void BayesDivide(const TH1* pass, const TH1* total, Option_t* option = "")
static TClass* Class()
virtual void ComputeRange(Double_t& xmin, Double_t& ymin, Double_t& xmax, Double_t& ymax) const
virtual Double_t GetErrorX(Int_t bin) const
virtual Double_t GetErrorXhigh(Int_t i) const
virtual Double_t GetErrorXlow(Int_t i) const
virtual Double_t GetErrorY(Int_t bin) const
virtual Double_t GetErrorYhigh(Int_t i) const
virtual Double_t GetErrorYlow(Int_t i) const
virtual Double_t* GetEXhigh() const
virtual Double_t* GetEXlow() const
virtual Double_t* GetEYhigh() const
virtual Double_t* GetEYlow() const
virtual TClass* IsA() const
TGraphAsymmErrors& operator=(const TGraphAsymmErrors& gr)
virtual void Paint(Option_t* chopt = "")
virtual void Print(Option_t* chopt = "") const
virtual void SavePrimitive(ostream& out, Option_t* option = "")
virtual void SetPointError(Double_t exl, Double_t exh, Double_t eyl, Double_t eyh)
virtual void SetPointError(Int_t i, Double_t exl, Double_t exh, Double_t eyl, Double_t eyh)
virtual void SetPointEXhigh(Int_t i, Double_t exh)
virtual void SetPointEXlow(Int_t i, Double_t exl)
virtual void SetPointEYhigh(Int_t i, Double_t eyh)
virtual void SetPointEYlow(Int_t i, Double_t eyl)
virtual void ShowMembers(TMemberInspector& insp, char* parent)
virtual void Streamer(TBuffer& b)
void StreamerNVirtual(TBuffer& b)
protected:
Double_t* fEXlow [fNpoints] array of X low errors
Double_t* fEXhigh [fNpoints] array of X high errors
Double_t* fEYlow [fNpoints] array of Y low errors
Double_t* fEYhigh [fNpoints] array of Y high errors
______________________________________________________________________________
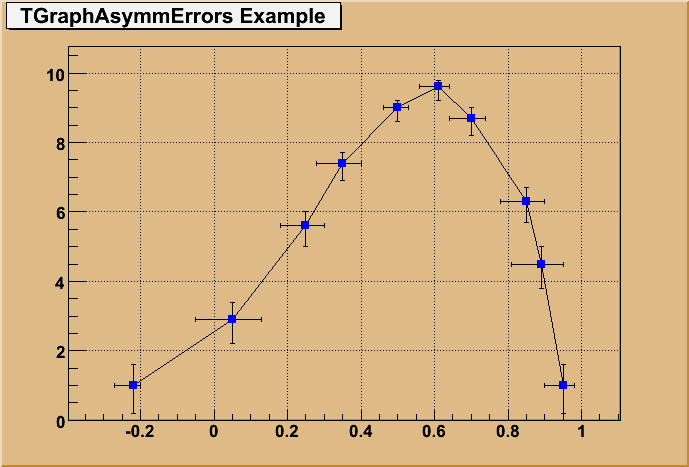
A TGraphAsymmErrors is a TGraph with assymetric error bars.
The various format options to draw a TGraphAsymmErrors are explained in
TGraphAsymmErrors::Paint.
The picture below has been generated by the following macro:
------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
gROOT->Reset();
c1 = new TCanvas("c1","A Simple Graph with error bars",200,10,700,500);
c1->SetFillColor(42);
c1->SetGrid();
c1->GetFrame()->SetFillColor(21);
c1->GetFrame()->SetBorderSize(12);
Int_t n = 10;
Double_t x[n] = {-0.22, 0.05, 0.25, 0.35, 0.5, 0.61,0.7,0.85,0.89,0.95};
Double_t y[n] = {1,2.9,5.6,7.4,9,9.6,8.7,6.3,4.5,1};
Double_t exl[n] = {.05,.1,.07,.07,.04,.05,.06,.07,.08,.05};
Double_t eyl[n] = {.8,.7,.6,.5,.4,.4,.5,.6,.7,.8};
Double_t exh[n] = {.02,.08,.05,.05,.03,.03,.04,.05,.06,.03};
Double_t eyh[n] = {.6,.5,.4,.3,.2,.2,.3,.4,.5,.6};
gr = new TGraphAsymmErrors(n,x,y,exl,exh,eyl,eyh);
gr->SetTitle("TGraphAsymmErrors Example");
gr->SetMarkerColor(4);
gr->SetMarkerStyle(21);
gr->Draw("ALP");
c1->Update();
}
TGraphAsymmErrors(const TVectorF &vx, const TVectorF &vy, const TVectorF &vexl, const TVectorF &vexh, const TVectorF &veyl, const TVectorF &veyh)
Constructor with six vectors of floats in input
A grapherrors is built with the X coordinates taken from vx and Y coord from vy
and the errors from vectors vexl/h and veyl/h.
The number of points in the graph is the minimum of number of points
in vx and vy.
TGraphAsymmErrors(const TVectorD &vx, const TVectorD &vy, const TVectorD &vexl, const TVectorD &vexh, const TVectorD &veyl, const TVectorD &veyh)
Constructor with six vectors of doubles in input
A grapherrors is built with the X coordinates taken from vx and Y coord from vy
and the errors from vectors vexl/h and veyl/h.
The number of points in the graph is the minimum of number of points
in vx and vy.
void Apply(TF1 *f)
apply a function to all data points
y = f(x,y)
Errors are calculated as eyh = f(x,y+eyh)-f(x,y) and
eyl = f(x,y)-f(x,y-eyl)
Special treatment has to be applied for the functions where the
role of "up" and "down" is reversed.
function suggested/implemented by Miroslav Helbich <helbich@mail.desy.de>
void BayesDivide(const TH1 *pass, const TH1 *total, Option_t *option)
Fills this TGraphAsymmErrors by dividing two input TH1 histograms pass/total.
Andy Haas (haas@fnal.gov)
University of Washington
Method and code directly taken from:
Marc Paterno (paterno@fnal.gov)
FNAL/CD
The input histograms must be filled with weights of 1.
By default the function does not check this assertion.
if option "w" is specified, the function will fail if the histograms
have been filled with weights not equal to 1.
The assumption is that the entries in "pass" are a
subset of those in "total". That is, we create an "efficiency"
graph, where each entry is between 0 and 1, inclusive.
The resulting graph can be fit to functions, using standard methods:
graph->Fit("erf")... for instance. (You have to define the erf
function for yourself for now, sorry.)
The points are assigned an x value at the center of each histogram bin.
The y values are #pass/#total, between 0 and 1.
The x errors span each histogram bin (lowedge->lowedge+width)
The y errors are the fun part. :)
The y errors are assigned based on applying Bayes theorem.
The model is the Binomial distribution, and the "prior" is
the flat distribution from 0 to 1.
If there is no data in a bin of the total histogram, no information
can be obtained for that bin, so no point is made on the graph.
The complete method and a beautiful discussion can be found here:
http://home.fnal.gov/~paterno/images/effic.pdf
And more information is on these pages:
http://home.fnal.gov/~paterno/probability/localresources.html
A backup of the main document is here:
http://www-clued0.fnal.gov/~haas/documents/paterno_effic.pdf
A 68.3% Confidence Level is used to assign the errors.
Warning! You should understand, the errors reported are the shortest
ranges containing 68.3% of the probability distrubution. The errors are
not exactly Gaussian! The Minuit fitting routines will assume that
the errors are Gaussian. But this is a reasonable approximation.
A fit using the full shape of the error distribution for each point
would be far more difficult to perform.
double Beta_ab(double a, double b, int k, int N)
Calculates the fraction of the area under the
curve x^k*(1-x)^(N-k) between x=a and x=b
double Ibetai(double a, double b, double x)
Calculates the incomplete beta function I_x(a,b); this is
the incomplete beta function divided by the complete beta function
double Betai(double a, double b, double x)
Calculates the incomplete beta function B_x(a,b), as defined
in Gradshteyn and Ryzhik (4th edition) 8.391
double Brent(double ax, double bx, double cx, double tol, double *xmin)
Implementation file for the numerical equation solver library.
This includes root finding and minimum finding algorithms.
Adapted from Numerical Recipes in C, 2nd edition.
Translated to C++ by Marc Paterno
void Efficiency(int k, int N, double conflevel, double& mode, double& low, double& high)
Calculate the shortest central confidence interval containing the required
probability content.
Interval(low) returns the length of the interval starting at low
that contains CONFLEVEL probability. We use Brent's method,
except in two special cases: when k=0, or when k=N
Main driver routine
Author: Marc Paterno
Double_t GetErrorX(Int_t i)
This function is called by GraphFitChisquare.
It returns the error along X at point i.
Double_t GetErrorY(Int_t i)
This function is called by GraphFitChisquare.
It returns the error along Y at point i.
double Interval(double low)
Return the length of the interval starting at low
that contains CONFLEVEL of the x^GLOBAL_k*(1-x)^(GLOBAL_N-GLOBAL_k)
distribution.
If there is no sufficient interval starting at low, we return 2.0
void Paint(Option_t *option)
Paint this TGraphAsymmErrors with its current attributes
by default horizonthal and vertical small lines are drawn at
the end of the error bars. if option "z" or "Z" is specified,
these lines are not drawn.
if option contains ">" an arrow is drawn at the end of the error bars
if option contains "|>" a full arrow is drawn at the end of the error bars
the size of the arrow is set to 2/3 of the marker size.
By default, error bars are drawn. If option "X" is specified,
the errors are not drawn (TGraph::Paint equivalent).
if option "[]" is specified only the end vertical/horizonthal lines
of the error bars are drawn. This option is interesting to superimpose
systematic errors on top of a graph with statistical errors.
if option "2" is specified error rectangles are drawn.
if option "3" is specified a filled area is drawn through the end points >
the vertical error bars.
if option "4" is specified a smoothed filled area is drawn through the end
points of the vertical error bars.
double SearchLower(double high, int k, int N, double c)
Integrates the binomial distribution with
parameters k,N, and determines what is the lower edge of the
integration region which ends at high, and which contains
probability content c. If a lower limit is found, the value is
returned. If no solution is found, the -1 is returned.
check to see if there is any solution by verifying that the integral down
to the minimum lower limit (0) is greater than c
double SearchUpper(double low, int k, int N, double c)
Integrates the binomial distribution with
parameters k,N, and determines what is the upper edge of the
integration region which starts at low which contains probability
content c. If an upper limit is found, the value is returned. If no
solution is found, -1 is returned.
check to see if there is any solution by verifying that the integral up
to the maximum upper limit (1) is greater than c
Author: Rene Brun 03/03/99
Last update: root/graf:$Name: $:$Id: TGraphAsymmErrors.cxx,v 1.60 2006/07/09 05:27:54 brun Exp $
Copyright (C) 1995-2000, Rene Brun and Fons Rademakers. *
ROOT page - Class index - Class Hierarchy - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
